Vanillic acid changed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedling rhizosphere total bacterial, Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. communities
- PMID: 29563548
- PMCID: PMC5862977
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-23406-2
Vanillic acid changed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedling rhizosphere total bacterial, Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. communities
Abstract
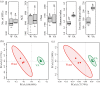
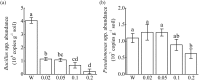
Soil microorganisms are key drivers of plant productivity in terrestrial ecosystems, yet controls on their diversities and abundances are not fully elucidated. Phenolic acids, released through plant root exudation and residues decomposition, are usually referred as autotoxins of several crops, including cucumber. In this study, effects of vanillic acid (VA) on cucumber rhizosphere microbial communities were investigated by treating cucumber seedlings with VA every two days for five times. Amplicon sequencing, PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative PCR were used to analyzed the 16S rRNA genes of total bacterial, Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. communities. Results showed that VA at 0.05 μmol g-1 soil changed total bacterial community diversity and composition. In particular, VA inhibited the relative abundances of genera with plant-beneficial potentials, such as Bacillus and Lysobacter spp. Moreover, VA changed Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. community compositions by altering the number and/or relative abundances of their OTUs; and decreased Bacillus spp. community abundance at 0.02 to 0.2 μmol g-1 soil and Pseudomonas spp. community abundance at 0.2 μmol g-1 soil. Overall, VA changed cucumber seedling rhizosphere total bacterial, Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. communities, which maybe be associated with the adverse effects of VA on cucumber growth under soil conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK. Autotoxicity: concept, organisms and ecological significance. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1999;18:757–772. doi: 10.1080/07352689991309478. - DOI
-
- Zhou X, Liu J, Wu F. Soil microbial communities in cucumber monoculture and rotation systems and their feedback effects on cucumber seedling growth. Plant Soil. 2017;415:507–520. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3181-5. - DOI
-
- Zhou X, Yu G, Wu F. Effects of intercropping cucumber with onion or garlic on soil enzyme activities, microbial communities and cucumber yield. Eur J Soil Biol. 2011;47:279–287. doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2011.07.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

