Comorbidities and treatment outcomes in multidrug resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29563561
- PMCID: PMC5862834
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-23344-z
Comorbidities and treatment outcomes in multidrug resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
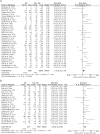
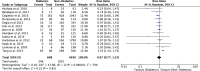
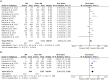
Little is known about the impact of comorbidities on multidrug resistant (MDR) and extensively drug resistant (XDR) tuberculosis (TB) treatment outcomes. We aimed to examine the effect of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), diabetes, chronic kidney disease (CKD), alcohol misuse, and smoking on MDR/XDRTB treatment outcomes. We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Registrar and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews as per PRISMA guidelines. Eligible studies were identified and treatment outcome data were extracted. We performed a meta-analysis to generate a pooled relative risk (RR) for unsuccessful outcome in MDR/XDRTB treatment by co-morbidity. From 2457 studies identified, 48 reported on 18,257 participants, which were included in the final analysis. Median study population was 235 (range 60-1768). Pooled RR of unsuccessful outcome was higher in people living with HIV (RR = 1.41 [95%CI: 1.15-1.73]) and in people with alcohol misuse (RR = 1.45 [95%CI: 1.21-1.74]). Outcomes were similar in people with diabetes or in people that smoked. Data was insufficient to examine outcomes in exclusive XDRTB or CKD cohorts. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, alcohol misuse and HIV were associated with higher pooled OR of an unsuccessful outcome in MDR/XDRTB treatment. Further research is required to understand the role of comorbidities in driving unsuccessful treatment outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis: Emergency update 2008.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2016 May 20]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43965/1/9789241547581_eng.pdf.
-
- The Global MDR-TB & XDR-TB Response Plan 2007–2008.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2016 May 20]. Available from: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/2007/global_response_plan.pdf.
-
- Laserson KF, et al. Speaking the same language: treatment outcome definitions for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. J Tuberc. 2005;9:640–645. - PubMed
-
- Bastos ML, et al. Treatment outcomes of patients with multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis according to drug susceptibility testing to first- and second-line drugs: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:1364–1374. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu619. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

