JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
- PMID: 29563586
- PMCID: PMC5862942
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03410-w
JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 23;9(1):1675. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04196-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29686330 Free PMC article.
Abstract
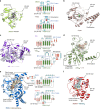
Oxygenase-catalysed post-translational modifications of basic protein residues, including lysyl hydroxylations and Nε-methyl lysyl demethylations, have important cellular roles. Jumonji-C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 5 (JMJD5), which genetic studies reveal is essential in animal development, is reported as a histone Nε-methyl lysine demethylase (KDM). Here we report how extensive screening with peptides based on JMJD5 interacting proteins led to the finding that JMJD5 catalyses stereoselective C-3 hydroxylation of arginine residues in sequences from human regulator of chromosome condensation domain-containing protein 1 (RCCD1) and ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6). High-resolution crystallographic analyses reveal overall fold, active site and substrate binding/product release features supporting the assignment of JMJD5 as an arginine hydroxylase rather than a KDM. The results will be useful in the development of selective oxygenase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer and genetic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

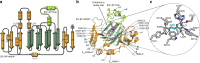



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

