Comparison of choroidal thickness using swept-source and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in normal Indian eyes
- PMID: 29563693
- PMCID: PMC5848346
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_27_2017
Comparison of choroidal thickness using swept-source and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in normal Indian eyes
Abstract
Background/aims: Choroidal thickness measurements are reported to differ between spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and swept-source OCT (SS-OCT). The aim of this study was to assess the comparability of choroidal thickness measurements using SS-OCT and SD-OCT devices among normal participants.
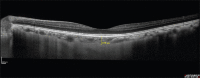
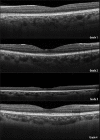
Materials and methods: This was a prospective study of 31 (62 eyes) normal participants. Choroidal imaging was performed sequentially with the Spectralis OCT (SD-OCT) and the deep range imaging OCT (DRI OCT-1) (SS-OCT) using standardized imaging protocols. The subfoveal choroidal thickness (SFChT) was measured manually by two masked retinal specialists. Paired t-tests and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were used to compare the measurements.
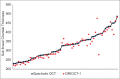
Results: The mean SFChT was 319.5 μm and 325.3 μm for DRI OCT-1 and Spectralis OCT, respectively (P = 0.001), with a mean difference of 5.9 with ICC of 0.97. The mean difference in choroidal thickness between the OCT devices was larger among eyes with choroidal thickness > 350 μm compared with eyes with thinner choroids (8.0 μm vs. 4.7 μm).
Conclusions: SFChT measurements are comparable between DRI OCT-1 and Spectralis OCT. The variability between the devices increases in thicker choroids.
Keywords: Choroidal thickness; spectral-domain optical coherence tomography; swept-source optical coherence tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parver LM. Temperature modulating action of choroidal blood flow. Eye (Lond) 1991;5(Pt 2):181–5. - PubMed
-
- Mertz JR, Wallman J. Choroidal retinoic acid synthesis: A possible mediator between refractive error and compensatory eye growth. Exp Eye Res. 2000;70:519–27. - PubMed
-
- McFadden SA, Howlett MH, Mertz JR. Retinoic acid signals the direction of ocular elongation in the guinea pig eye. Vision Res. 2004;44:643–53. - PubMed
-
- Kuroda S, Ikuno Y, Yasuno Y, Nakai K, Usui S, Sawa M, et al. Choroidal thickness in central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 2013;33:302–8. - PubMed

