Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 as a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29563759
- PMCID: PMC5850134
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i10.1152
Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 as a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the clinicopathological significance of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) and PGRMC2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
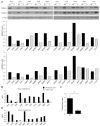
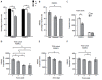
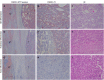
Methods: We performed immunohistochemical staining to evaluate the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), PGRMC1, and PGRMC2 in a clinical cohort consisting of 89 paired HCC and non-tumor liver samples. We also analyzed HCC data (n = 373) from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We correlated the expression status of PGRMC1 and PGRMC2 with clinicopathological indicators and the clinical outcomes of the HCC patients. We knocked down or overexpressed PGRMC1 in HCC cell lines to evaluate its biological significance in HCC cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and invasion.
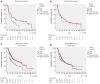
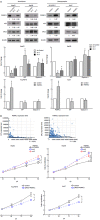
Results: We found that few HCC cases expressed ER (5.6%) and PR (4.5%). In contrast, most HCC cases expressed PGRMC1 (89.9%) and PGRMC2 (100%). PGRMC1 and PGRMC2 exhibited significantly lower expression in tumor tissue than in non-tumor tissue (P < 0.001). Lower PGRMC1 expression in HCC was significantly associated with higher serum alpha-fetoprotein expression (P = 0.004), poorer tumor differentiation (P = 0.045) and liver capsule penetration (P = 0.038). Low PGRMC1 expression was an independent predictor for worse disease-free survival (P = 0.002, HR = 2.384, CI: 1.377-4.128) in our cases, as well as in the TCGA cohort (P < 0.001, HR = 2.857, CI: 1.781-4.584). The expression of PGRMC2 did not relate to patient outcome. PGRMC1 knockdown promoted a poorly differentiated phenotype and proliferation of HCC cells in vitro, while PGRMC1 overexpression caused the opposite effects.
Conclusion: PGRMC1 is a non-classical hormonal receptor that negatively regulates hepatocarcinogenesis. PGRMC1 down-regulation is associated with progression of HCC and is a poor prognostic indicator.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Hormonal receptor; Progesterone receptor membrane component 1; Prognosis; Proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuron-glial antigen 2 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poor prognosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 7;21(21):6649-59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6649. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26074703 Free PMC article.
-
Fibulin-5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 12;14:938. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-938. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25494879 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of nuclear progesterone receptor and progesterone receptor membrane components 1 and 2 in the oviduct of cyclic and pregnant cows during the post-ovulation period.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012 Sep 7;10:76. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-10-76. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22958265 Free PMC article.
-
The association of HMGB1 expression with clinicopathological significance and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis and literature review.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 30;9(10):e110626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110626. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25356587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of alanine-glyoxylate and serine-pyruvate aminotransferase expression accelerated the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and predicted poor prognosis.J Transl Med. 2019 Nov 26;17(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02138-5. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31771612 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive multi-level expression profiling of key biomarkers in breast cancer patients.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Oct 15;15(10):6058-6070. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37969199 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of PGRMC1 Delays the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Suppression of Pro-Inflammatory Immune Responses.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 18;13(10):2438. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102438. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069911 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Evaluation of Cell Culture Systems for Hepatitis E Virus.Viruses. 2022 Jun 9;14(6):1254. doi: 10.3390/v14061254. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35746725 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-ray irradiation modulates PGRMC1 expression and the number of CD56+ and FoxP3+ cells in the tumor microenvironment of endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma.Radiat Oncol J. 2021 Dec;39(4):324-333. doi: 10.3857/roj.2021.00472. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Radiat Oncol J. 2021. PMID: 34986554 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone suppresses the progression of colonic carcinoma by increasing the activity of the GADD45α/JNK/c‑Jun signalling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2021 Jun;45(6):95. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8046. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33846816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Chang WT, Hsieh BS, Cheng HL, Lee KT, Chang KL. Progesterone augments epirubicin-induced apoptosis in HA22T/VGH cells by increasing oxidative stress and upregulating Fas/FasL. J Surg Res. 2014;188:432–441. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

