Development of small bisquaternary cholinesterase inhibitors as drugs for pre-treatment of nerve agent poisonings
- PMID: 29563775
- PMCID: PMC5849933
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S133038
Development of small bisquaternary cholinesterase inhibitors as drugs for pre-treatment of nerve agent poisonings
Abstract
Background: Intoxication by nerve agents could be prevented by using small acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (eg, pyridostigmine) for potentially exposed personnel. However, the serious side effects of currently used drugs led to research of novel potent molecules for prophylaxis of organophosphorus intoxication.
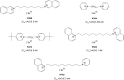
Methods: The molecular design, molecular docking, chemical synthesis, in vitro methods (enzyme inhibition, cytotoxicity, and nicotinic receptors modulation), and in vivo methods (acute toxicity and prophylactic effect) were used to study bispyridinium, bisquinolinium, bisisoquinolinium, and pyridinium-quinolinium/isoquinolinium molecules presented in this study.
Results: The studied molecules showed non-competitive inhibitory ability towards human acetylcholinesterase in vitro that was further confirmed by molecular modelling studies. Several compounds were selected for further studies. First, their cytotoxicity, nicotinic receptors modulation, and acute toxicity (lethal dose for 50% of laboratory animals [LD50]; mice and rats) were tested to evaluate their safety with promising results. Furthermore, their blood levels were measured to select the appropriate time for prophylactic administration. Finally, the protective ratio of selected compounds against soman-induced toxicity was determined when selected compounds were found similarly potent or only slightly better to standard pyridostigmine.
Conclusion: The presented small bisquaternary molecules did not show overall benefit in prophylaxis of soman-induced in vivo toxicity.
Keywords: AChE inhibitors; nerve agents; pre-treatment; prophylaxis; soman; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
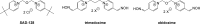

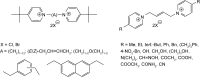
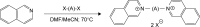

References
-
- Marrs TC. Organophosphate anticholinesterase poisoning. Toxic Subst Mech. 1996;15:357–388.
-
- Bajgar J, Fusek J, Kuca K, Bartosova L, Jun D. Treatment of organophosphate intoxication using cholinesterase reactivators: facts and fiction. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007;7(5):461–466. - PubMed
-
- Patocka J, Jun D, Bajgar J, Kuca K. Prophylaxis against nerve agent intoxications. Def Sci J. 2006;56:775–784.
-
- Masson P, Josse D, Lockridge O, Viguie N, Taupin C, Buhler C. Enzymes hydrolyzing organophosphates as potential catalytic scavengers against organophosphate poisoning. J Physiol Paris. 1998;92(5–6):357–362. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

