Pomegranate extract-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: design, optimization, and in vitro cytotoxicity study
- PMID: 29563789
- PMCID: PMC5846752
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S154033
Pomegranate extract-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: design, optimization, and in vitro cytotoxicity study
Abstract
Background: Pomegranate extract (PE) is a natural product with potent antioxidant and anticancer activity because of its polyphenols content. The main purpose of this study was to maximize the PE chemotherapeutic efficacy by loading it in an optimized solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) formula.
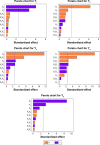
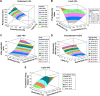
Materials and methods: The influence of independent variables, which were lipid concentration (X1), surfactant concentration (X2) and cosurfactant concentration (X3), on dependent ones, which were particle size (Y1), polydispersity index (Y2), zeta potential (Y3), entrapment efficiency (Y4) and cumulative % drug release (Y5), were studied and optimized using the Box-Behnken design. Fifteen formulations of PE-SLNs were prepared using hot homogenization followed by ultra-sonication technique. Response surface plots, Pareto charts and mathematical equations were produced to study the impact of independent variables on the dependent quality parameters. The anti-proliferative activity of the optimized formula was then evaluated in three different cancer cell lines, namely, MCF-7, PC-3 and HepG-2, in addition to one normal cell line, HFB-4.
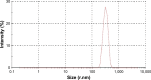
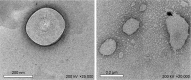
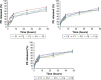
Results: The results demonstrated that the particle sizes ranged from 407.5 to 651.9 nm and the entrapment efficiencies ranged from 56.02 to 65.23%. Interestingly, the 50% inhibitory concentration of the optimized formula had more than a 40-fold improved effect on the cell growth inhibition in comparison with its free counterpart. Furthermore, it was more selective against cancer cells than normal cells particularly in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: These data proved that nanoencapsulation of PE enhanced its anticancer efficacy. Therefore, our results suggested that a PE-loaded SLNs optimized-formula could be a promising chemo therapeutic agent.
Keywords: Box-Behnken design; cancer cell lines; optimization; pomegranate extract; solid lipid nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natamycin solid lipid nanoparticles - sustained ocular delivery system of higher corneal penetration against deep fungal keratitis: preparation and optimization.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Apr 8;14:2515-2531. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S190502. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31040672 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Pomegranate Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Quality by Design Approach to Screen the Variables Affecting the Quality Attributes and Characterization.ACS Omega. 2020 Aug 17;5(34):21712-21721. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02618. eCollection 2020 Sep 1. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32905321 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of Morus alba extract loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: in silico, characterizations, and in vitro cytotoxicity study.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025 Jan;51(1):14-28. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2024.2439930. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39651657
-
Optimization of methazolamide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for ophthalmic delivery using Box-Behnken design.J Liposome Res. 2014 Sep;24(3):171-81. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2014.891231. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Liposome Res. 2014. PMID: 24611687 Review.
-
Cholesterylbutyrate solid lipid nanoparticles as a butyric acid prodrug.Molecules. 2008 Feb 1;13(2):230-54. doi: 10.3390/molecules13020230. Molecules. 2008. PMID: 18305415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zein/Phospholipid Composite Nanoparticles for Successful Delivery of Gallic Acid into aHSCs: Influence of Size, Surface Charge, and Vitamin A Coupling.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 16;15:7995-8018. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S270242. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116514 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs and Herbal Medicines in the Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2022;10(5):342-353. doi: 10.2174/2211738510666220831113857. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36045536 Review.
-
Pomegranate-specific natural compounds as onco-preventive and onco-therapeutic compounds: Comparison with conventional drugs acting on the same molecular mechanisms.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 8;9(7):e18090. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18090. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37519687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols as Antioxidants for Extending Food Shelf-Life and in the Prevention of Health Diseases: Encapsulation and Interfacial Phenomena.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 14;9(12):1909. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121909. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and characterization of Agarwood extract-loaded nanocapsules and evaluation of their toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity on RAW 264.7 cells and in zebrafish embryos.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2618-2633. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2012307. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34894947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thurston DE. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2006.
-
- Jagtap S, Meganathan K, Wagh V, Winkler J, Hescheler J, Sachinidis A. Chemoprotective mechanism of the natural compounds, epigallocatechin- 3-O-gallate, quercetin and curcumin against cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(12):1451–1462. - PubMed
-
- Lee KW, Bode AM, Dong Z. Molecular targets of phytochemicals for cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(3):211–218. - PubMed
-
- Jurenka JS. Therapeutic applications of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.): a review. Altern Med Rev. 2008;13(2):128–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

