Decreased health-related quality of life in patients with diabetic foot problems
- PMID: 29563821
- PMCID: PMC5846758
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S154304
Decreased health-related quality of life in patients with diabetic foot problems
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with diabetic foot problems and compare the HRQoL between diabetic patients with: 1) diabetic foot problems (DF), including diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) or amputation (AMPU); 2) other diabetic complications (COM), such as diabetic retinopathy (DR), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), or coronary artery disease (CAD); and 3) no diabetic complication (CON).
Patients and methods: A total of 254 diabetic patients were studied in a cross-sectional setting. HRQoL was evaluated using Thai version of the Euro Quality of Life Questionnaire (EuroQoL), with five dimensions and five-level scale (EQ-5D-5L). Utility scores were calculated using time trade-off methods.
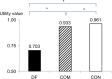
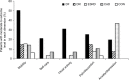
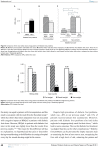
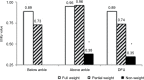
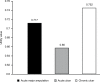
Results: A total of 141 patients in the DF group (98 DFU and 43 AMPU groups), 82 in the COM group (27 DR, 28 ESRD, and 27 CAD groups), and 31 in the CON group were interviewed. The mean age was 63.2±12.1 years, body mass index was 24.9±4.7 kg/m2, mean hemoglobin A1c was 7.7±2.1%, duration of diabetes was 13.1±9.9 years, and the mean utility scores were 0.799±0.25. After having DF, 21% of patients had lost their jobs. The COM group had lower utility scores than the CON group. Among the diabetic complications, the DF group had the lowest mean utility scores as compared to the COM and CON groups (0.703±0.28 in the DF group, 0.903±0.15 in the COM group, and 0.961±0.06 in the CON group, P<0.01). There was no difference in the mean utility scores between DFU and AMPU groups. Patients in the DF group reported moderate-to-severe problem in all dimensions more than the other groups.
Conclusion: DF have the greatest negative impact on HRQoL. Therefore, diabetic foot care should be emphasized in clinical practice to prevent foot complications.
Keywords: diabetic complications; diabetic foot problems; health-related quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Bureau of Epidemiology, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand Chronic Diseases Surveillance Report 2012. [Accessed November 15, 2017]. Available from: http://www.boe.moph.go.th/files/report/20140109_40197220.pdf.
-
- Bureau of Policy and Strategy, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand Statistical Thailand 2014. [Accessed November 15, 2017]. Available from: http://bps.moph.go.th/new_bps/sites/default/files/health_statistics2557.pdf.
-
- Brod M. Quality of life issues in patients with diabetes and lower extremity ulcer: patients and caregivers. Qual Life Res. 1998;91:733–737. - PubMed
-
- Price P. The diabetic foot: quality of life. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(Suppl 2):S129–S131. - PubMed
-
- Redekop WK, Stolk EA, Kok E, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers and amputations: estimates of health utility for use in cost effectiveness analyses of new treatments. Diabetes Metab. 2004;30:549–556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

