Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective
- PMID: 29563876
- PMCID: PMC5845960
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00203
Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective
Abstract
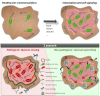
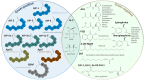
Numerous bacteria utilize molecular communication systems referred to as quorum sensing (QS) to synchronize the expression of certain genes regulating, among other aspects, the expression of virulence factors and the synthesis of biofilm. To achieve this process, bacteria use signaling molecules, known as autoinducers (AIs), as chemical messengers to share information. Naturally occurring strategies that interfere with bacterial signaling have been extensively studied in recent years, examining their potential to control bacteria. To interfere with QS, bacteria use quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) to block the action of AIs and quorum quenching (QQ) enzymes to degrade signaling molecules. Recent studies have shown that these strategies are promising routes to decrease bacterial pathogenicity and decrease biofilms, potentially enhancing bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobial agents including antibiotics and bacteriophages. The efficacy of QSIs and QQ enzymes has been demonstrated in various animal models and are now considered in the development of new medical devices against bacterial infections, including dressings, and catheters for enlarging the therapeutic arsenal against bacteria.
Keywords: antibioresistance; bacterial virulence; biofilm; medical devices; phage resistance; quorum quenching enzymes; quorum sensing (QS); quorum sensing inhibitors.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

