A Systematic Evaluation of the Two-Component Systems Network Reveals That ArlRS Is a Key Regulator of Catheter Colonization by Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 29563900
- PMCID: PMC5845881
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00342
A Systematic Evaluation of the Two-Component Systems Network Reveals That ArlRS Is a Key Regulator of Catheter Colonization by Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
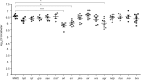
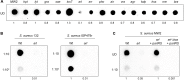
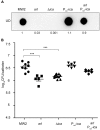
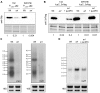
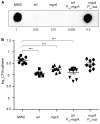
Two-component systems (TCS) are modular signal transduction pathways that allow cells to adapt to prevailing environmental conditions by modifying cellular physiology. Staphylococcus aureus has 16 TCSs to adapt to the diverse microenvironments encountered during its life cycle, including host tissues and implanted medical devices. S. aureus is particularly prone to cause infections associated to medical devices, whose surfaces coated by serum proteins constitute a particular environment. Identification of the TCSs involved in the adaptation of S. aureus to colonize and survive on the surface of implanted devices remains largely unexplored. Here, using an in vivo catheter infection model and a collection of mutants in each non-essential TCS of S. aureus, we investigated the requirement of each TCS for colonizing the implanted catheter. Among the 15 mutants in non-essential TCSs, the arl mutant exhibited the strongest deficiency in the capacity to colonize implanted catheters. Moreover, the arl mutant was the only one presenting a major deficit in PNAG production, the main exopolysaccharide of the S. aureus biofilm matrix whose synthesis is mediated by the icaADBC locus. Regulation of PNAG synthesis by ArlRS occurred through repression of IcaR, a transcriptional repressor of icaADBC operon expression. Deficiency in catheter colonization was restored when the arl mutant was complemented with the icaADBC operon. MgrA, a global transcriptional regulator downstream ArlRS that accounts for a large part of the arlRS regulon, was unable to restore PNAG expression and catheter colonization deficiency of the arlRS mutant. These findings indicate that ArlRS is the key TCS to biofilm formation on the surface of implanted catheters and that activation of PNAG exopolysaccharide production is, among the many traits controlled by the ArlRS system, a major contributor to catheter colonization.
Keywords: PNAG; Staphylococcus aureus; arlRS; biofilm; implants; two-component systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus develops an alternative, ica-independent biofilm in the absence of the arlRS two-component system.J Bacteriol. 2005 Aug;187(15):5318-29. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.15.5318-5329.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16030226 Free PMC article.
-
σB Inhibits Poly-N-Acetylglucosamine Exopolysaccharide Synthesis and Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2019 May 8;201(11):e00098-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00098-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30858304 Free PMC article.
-
The two-component signal transduction system ArlRS regulates Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation in an ica-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040041. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848368 Free PMC article.
-
Function and regulation of Staphylococcus aureus wall teichoic acids and capsular polysaccharides.Int J Med Microbiol. 2019 Sep;309(6):151333. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.151333. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Int J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31362856 Review.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system regulates virulence factor expression through MgrA.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Jan;113(1):103-122. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14404. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31618469 Free PMC article.
-
The Ability of Lytic Staphylococcal Podovirus vB_SauP_phiAGO1.3 to Coexist in Equilibrium With Its Host Facilitates the Selection of Host Mutants of Attenuated Virulence but Does Not Preclude the Phage Antistaphylococcal Activity in a Nematode Infection Model.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 18;9:3227. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03227. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30713528 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of two-component sensorial network in staphylococcal speciation.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020 Jun;55:40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2020.02.004. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32199334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glabridin Averts Biofilms Formation in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Modulation of the Surfaceome.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 17;11:1779. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01779. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33071991 Free PMC article.
-
The Sensor Histidine Kinase ArlS Is Necessary for Staphylococcus aureus To Activate ArlR in Response to Nutrient Availability.J Bacteriol. 2021 Nov 19;203(24):e0042221. doi: 10.1128/JB.00422-21. Epub 2021 Oct 4. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34606376 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

