Old Yellow Enzyme from Trypanosoma cruzi Exhibits In Vivo Prostaglandin F2α Synthase Activity and Has a Key Role in Parasite Infection and Drug Susceptibility
- PMID: 29563916
- PMCID: PMC5845897
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00456
Old Yellow Enzyme from Trypanosoma cruzi Exhibits In Vivo Prostaglandin F2α Synthase Activity and Has a Key Role in Parasite Infection and Drug Susceptibility
Abstract
The discovery that trypanosomatids, unicellular organisms of the order Kinetoplastida, are capable of synthesizing prostaglandins raised questions about the role of these molecules during parasitic infections. Multiple studies indicate that prostaglandins could be related to the infection processes and pathogenesis in trypanosomatids. This work aimed to unveil the role of the prostaglandin F2α synthase TcOYE in the establishment of Trypanosoma cruzi infection, the causative agent of Chagas disease. This chronic disease affects several million people in Latin America causing high morbidity and mortality. Here, we propose a prokaryotic evolutionary origin for TcOYE, and then we used in vitro and in vivo experiments to show that T. cruzi prostaglandin F2α synthase plays an important role in modulating the infection process. TcOYE overexpressing parasites were less able to complete the infective cycle in cell culture infections and increased cardiac tissue parasitic load in infected mice. Additionally, parasites overexpressing the enzyme increased PGF2α synthesis from arachidonic acid. Finally, an increase in benznidazole and nifurtimox susceptibility in TcOYE overexpressing parasites showed its participation in activating the currently anti-chagasic drugs, which added to its observed ability to confer resistance to hydrogen peroxide, highlights the relevance of this enzyme in multiple events including host-parasite interaction.
Keywords: Old Yellow Enzyme; Trypanosoma cruzi; benznidazol and nifurtimox activation; differentially expressed gene; prostaglandin F2α synthase.
Figures

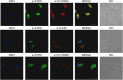
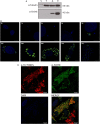


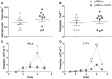

Similar articles
-
Deletion of copies of the gene encoding old yellow enzyme (TcOYE), a NAD(P)H flavin oxidoreductase, associates with in vitro-induced benznidazole resistance in Trypanosoma cruzi.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006 Apr;146(2):151-62. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2005.12.001. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16442642
-
A key role for old yellow enzyme in the metabolism of drugs by Trypanosoma cruzi.J Exp Med. 2002 Nov 4;196(9):1241-51. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020885. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12417633 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic diversity and drug susceptibility of Trypanosoma cruzi TcV clinical isolates.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 5;13(9):e0203462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203462. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30183775 Free PMC article.
-
Chagas disease: Present status of pathogenic mechanisms and chemotherapy.Biol Res. 2010;43(3):323-31. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Biol Res. 2010. PMID: 21249304 Review.
-
Aspects of Trypanosoma cruzi stage differentiation.Adv Parasitol. 2011;75:285-305. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385863-4.00013-7. Adv Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21820561 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights into the Role of the Trypanosoma cruzi Aldo-Keto Reductase TcAKR.Pathogens. 2023 Jan 5;12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010085. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36678433 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Four Mexican Isolates of Trypanosoma cruzi and Their Profile Susceptibility to Nifurtimox.Acta Parasitol. 2022 Dec;67(4):1584-1593. doi: 10.1007/s11686-022-00608-3. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Acta Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 36029434
-
Defeating the trypanosomatid trio: proteomics of the protozoan parasites causing neglected tropical diseases.RSC Med Chem. 2020 May 22;11(6):625-645. doi: 10.1039/d0md00122h. eCollection 2020 Jun 1. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33479664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Thermophilic Ene-Reductase from the Filamentous Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacterium Chloroflexus aggregans.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 28;9(5):953. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9050953. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33925162 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of multiple copies of the Prostaglandin F2alpha synthase gene affects oxidative stress response and infectivity in Trypanosoma cruzi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Oct 19;16(10):e0010845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010845. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36260546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanowitz HB, Wen JJ, Machado FS, Desruisseaux MS, Robello C, Garg NJ. Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas disease: innate immunity, ROS, and cardiovascular system. In: Gavins NE, Stokes KY, editors. Vascular Responses to Pathogens. Waltham, MA: Academic Press/Elsevier Inc. (2016). p. 183–93.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

