Evaluating the Fat Distribution in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Using Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Scanning
- PMID: 29563954
- PMCID: PMC5858863
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2017.1334218
Evaluating the Fat Distribution in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Using Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Scanning
Abstract
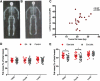
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is strongly associated with obesity. We aimed to utilise dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) to characterise fat distribution, and to evaluate change in fat mass and distribution following weight loss. IIH patients (n = 24) had a similar fat distribution to body mass index (BMI)- and gender-matched obese controls (n = 47). In the IIH cohort, truncal fat mass correlated with lumbar puncture pressure. Weight loss in IIH patients resulted in a significant reduction in disease activity and fat mass, predominantly from the truncal region (-4.40 ± 1.6%; p = 0.008) compared with the limbs (+0.79 ± 6.5%; p = 0.71). These results indicate that, contrary to previous studies using waist-hip ratios, IIH adiposity is centripetal, similar to simple obesity. Future studies should establish the risk of the metabolic syndrome and the role of adipose tissue depot-specific function in IIH.
Keywords: DEXA; idiopathic intracranial hypertension; obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is associated with lower body adiposity.Ophthalmology. 2010 Jan;117(1):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.06.030. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 19913917
-
The obesity pattern of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in men.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013 Nov;251(11):2643-6. doi: 10.1007/s00417-013-2420-6. Epub 2013 Aug 18. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23955783
-
Cerebrospinal fluid opening pressure: The effect of body mass index and body composition.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Jan;188:105597. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105597. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31778875
-
Obesity and Weight Loss in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Narrative Review.J Neuroophthalmol. 2017 Jun;37(2):197-205. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000000448. J Neuroophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27636748 Review.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical update on regulation of intracranial pressure in relation to idiopathic intracranial hypertension.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019 Nov 26;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12987-019-0155-4. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019. PMID: 31767019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiometabolic Outcomes in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: An International Matched-Cohort Study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 13:2024.11.12.24317203. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.12.24317203. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39677466 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Apr 16;25(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01420-y. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40237861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determining the role of novel metabolic pathways in driving intracranial pressure reduction after weight loss.Brain Commun. 2023 Oct 18;5(5):fcad272. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad272. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 37901040 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring The Current Management Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension, And Understanding The Role Of Dural Venous Sinus Stenting.Eye Brain. 2020 Jan 14;12:1-13. doi: 10.2147/EB.S193027. eCollection 2020. Eye Brain. 2020. PMID: 32021528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Markey KA, Mollan SP, Jensen RH, Sinclair AJ.. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:78–91. - PubMed
-
- Corbett JJ, Savino PJ, Thompson HS, Kansu T, Schatz NJ, Orr LS, Hopson D.. Visual loss in pseudotumor cerebri. Follow-up of 57 patients from five to 41 years and a profile of 14 patients with permanent severe visual loss. Arch Neurol 1982;39:461–474. - PubMed
-
- Sugerman HJ, DeMaria EJ, Felton WL. 3rd, Nakatsuka M, Sismanis A. Increased intra-abdominal pressure and cardiac filling pressures in obesity-associated pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 1997;49:507–511. - PubMed
-
- Manolopoulos KN, Karpe F, Frayn KN.. Gluteofemoral body fat as a determinant of metabolic health. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010;34:949–959. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
