Protective effects of paeonol on subacute/chronic brain injury during cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 29563983
- PMCID: PMC5858057
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5893
Protective effects of paeonol on subacute/chronic brain injury during cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
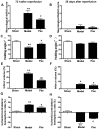
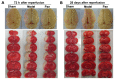
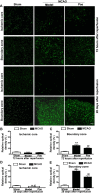
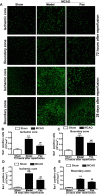
Ischemic stroke is a highly complex pathological process that is divided into acute, subacute and chronic phases. Paeonol is a biologically active natural product with a variety of pharmacological effects, including those on neuronal activity. However, the effects of paeonol on subacute/chronic ischemic stroke have remained to be elucidated. The present study was designed to investigate the effects of paeonol against subacute and chronic cerebral ischemic injury and to explore the possible underlying mechanisms. Male adult Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into a sham group (treated with saline), a model group [subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and treated with saline] and a paeonol-treated group (MCAO + paeonol at 25 mg/kg). Behavioral impairment, infarct volume and ischemic/contralateral hemispheric ratios were assessed at 72 h and at 28 days after MCAO, respectively. Immunofluorescence was employed to determine the neuronal damage and glial responses after MCAO. Compared with the model group, paeonol treatment significantly attenuated behavioral impairment, ischemic infarct volume and moderate cerebral edema in the ischemic brain at 72 h, as well as brain atrophy at 28 days after reperfusion. Furthermore, paeonol treatment ameliorated neuronal damage in the ischemic core and boundary zone regions at 72 h after reperfusion and in the boundary zone at 28 days after reperfusion. In addition, paeonol treatment reduced the proliferation of astrocytes in the boundary zone, and inhibited microglial activation in the ischemic core and boundary zone regions at 72 h and 28 days after reperfusion. These results demonstrated the protective effects of paeonol against subacute/chronic cerebral ischemia, and the mechanism of action may include subacute/chronic microglial activation and astrocyte proliferation.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia; paeonol; rat; subacute/chronic brain injury.
Figures

References
-
- Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP, Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW, Jr, Qureshi AI, Rosenfield K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44:870–947. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e318284056a. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
