Correlation between the expression of Drp1 in vascular endothelial cells and inflammatory factors in hypertension rats
- PMID: 29563985
- PMCID: PMC5858055
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5899
Correlation between the expression of Drp1 in vascular endothelial cells and inflammatory factors in hypertension rats
Abstract
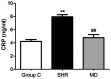
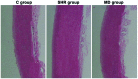
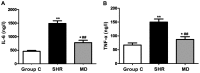
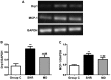
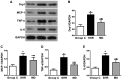
The objective of this study was to investigate the expression level of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) in vascular endothelium of hypertension rats and its correlation with expression of inflammatory factors. Twenty spontaneous hypertension rats (SHR) were randomly divided into SHR group (n=10) and inhibition group (MD group, n=10), and the Sprague Dawley rats were enrolled as the control group (C group, n=10). For rats in the MD group, Mdivi-1, a mitochondrial division inhibitor, was given in dosage of 25 mg/kg. After 4 weeks of administration, blood pressure was measured via tail-artery blood pressure measurement. The blood samples collected from the abdominal aorta of rats were used to assay the C-reaction protein (CRP) concentration in serum through radioimmunoassay. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was performed for sections of thoracic aorta for morphological observation and measurement of medial thickness. Enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA), semi-quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blotting was carried out for detecting the expression levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Drp1 and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1). After 4 weeks of drug administration, the blood pressure in the MD group was significantly higher (P<0.01). The medial thickness of the thoracic aorta in the MD group was significantly decreased in comparison with the SHR group (P<0.01). The results of ELISA showed that compared with the SHR group, the expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the MD group were remarkably decreased (P<0.01). Semi-quantitative RT-PCR results indicated that the mRNA expression levels of Drp1 and MCP-1 in the MD group were significantly lower than those in the SHR group (P<0.05). In the SHR rats, after administration of Mdivi-1, the expression of Drp1 is decreased, which contributes to the alleviation in inflammatory reactions and protects the vessels in SHR rats.
Keywords: dynamin-related protein 1; inflammatory factors; spontaneous hypertension rat; vessels.
Figures

References
-
- Song CL, Zhang X, Liu YK, Yue WW, Wu H. Heart rate turbulence in masked hypertension and white-coat hypertension. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:1457–1460. - PubMed
-
- Misárková E, Behuliak M, Bencze M, Zicha J. Excitation-contraction coupling and excitation-transcription coupling in blood vessels: Their possible interactions in hypertensive vascular remodeling. Physiol Res. 2016;65:173–191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
