Insulin alleviates mitochondrial oxidative stress involving upregulation of superoxide dismutase 2 and uncoupling protein 2 in septic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29563990
- PMCID: PMC5858081
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5890
Insulin alleviates mitochondrial oxidative stress involving upregulation of superoxide dismutase 2 and uncoupling protein 2 in septic acute kidney injury
Abstract
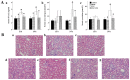
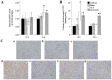
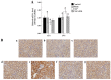
The aim of the present study was to explore the effects and mechanisms of insulin on mitochondrial oxidative stress in septic acute kidney injury (AKI). Male Sprague Dawley rats were divided randomly into four groups: Control group, sham surgery group, cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) group, and CLP plus insulin group. Blood specimens and kidney tissues were obtained at 12 and 24 h after surgery as separate experiments. Analyses of histology and indicators of renal injury [blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (CRE) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL)], mitochondrial function [adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP)], oxidative stress [inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO)], endogenous antioxidant systems [superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH)] as well as the expression of uncoupling protein (UCP), PINK1 protein (a major mediator of mitophagy), PGC1α protein (a major regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis) were performed. Compared with CLP group, the CLP plus insulin group had milder histological damage, higher levels of ATP and MMP as well as lower levels of BUN, serum CRE and NGAL, intrarenal iNOS, mitochondrial ROS and total NO. Moreover, the CLP plus insulin group demonstrated increased expression of SOD2 and UCP2. In contrast, insulin administration suppressed mitophagy meanwhile did not upregulate total GSH and induce mitochondrial biogenesis following CLP. These findings indicated that the upregulation of SOD2 and UCP2 may be involved in insulin protecting against mitochondrial oxidative stress in septic AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; endogenous antioxidant system; insulin; mitochondrial biogenesis; mitochondrial dysfunction; mitophagy; oxidative stress; sepsis; uncoupling protein 2.
Figures

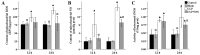




Similar articles
-
[Protective effects of Klotho protein on acute kidney injury in septic mice and its mechanism].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):160-164. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827302 Chinese.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin attenuates injury in the rat cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis via apoptosis inhibition.Nephrology (Carlton). 2015 Sep;20(9):646-53. doi: 10.1111/nep.12498. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015. PMID: 25943501
-
β-Casomorphin-7 Ameliorates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Targeting NF-κB Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jan 5;25:121-127. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912730. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30610183 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese Superoxide Dismutase Dysfunction and the Pathogenesis of Kidney Disease.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 14;11:755. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00755. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32760286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Oxidative Stress in Septic Acute Kidney Injury: From Theory to Practice.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 25;10(17):3798. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173798. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34501245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UCP2 silencing aggravates mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocytes under septic conditions.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Nov;20(5):4459-4466. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10721. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31702042 Free PMC article.
-
NEAT1 Confers Radioresistance to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inducing PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 19;23(22):14397. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214397. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430876 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effects of Perindopril Against Acute Kidney Damage Caused by Septic Shock.Inflammation. 2021 Feb;44(1):148-159. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01316-8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 32803666
-
Role of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in Sepsis.Acute Crit Care. 2018 May;33(2):65-72. doi: 10.4266/acc.2018.00157. Epub 2018 May 31. Acute Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 31723865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in septic acute kidney injury.Burns Trauma. 2023 Mar 20;11:tkad008. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkad008. eCollection 2023. Burns Trauma. 2023. PMID: 36959845 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
