Severity and burden of hand, foot and mouth disease in Asia: a modelling study
- PMID: 29564154
- PMCID: PMC5859810
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2017-000442
Severity and burden of hand, foot and mouth disease in Asia: a modelling study
Abstract
Background: Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) affects millions of children across Asia annually, leading to an increase in implemented control policies such as surveillance, isolation and social distancing in affected jurisdictions. However, limited knowledge of disease burden and severity causes difficulty in policy optimisation as the associated economic cost cannot be easily estimated. We use a data synthesis approach to provide a comprehensive picture of HFMD disease burden, estimating infection risk, symptomatic rates, the risk of complications and death, and overall disability-adjusted life-year (DALY) losses, along with associated uncertainties.
Methods: Complementary data from a variety of sources were synthesised with mathematical models to obtain estimates of severity of HFMD. This includes serological and other data extracted through a systematic review of HFMD epidemiology previously published by the authors, and laboratory investigations and sentinel reports from Singapore's surveillance system.
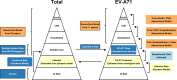
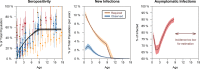
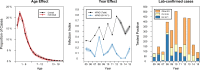
Results: HFMD is estimated to cause 96 900 (95% CI 40 600 to 259 000) age-weighted DALYs per annum in eight high-burden countries in East and Southeast Asia, with the majority of DALYs attributed to years of life lost. The symptomatic case hospitalisation rate of HFMD is 6% (2.8%-14.9%), of which 18.7% (6.7%-31.5%) are expected to develop complications. 5% (2.9%-7.4%) of such cases are fatal, bringing the overall case fatality ratio to be 52.3 (24.4-92.7) per 100 000 symptomatic infections. In contrast, the EV-A71 case fatality ratio is estimated to be at least 229.7 (75.4-672.1) per 100 000 symptomatic cases. Asymptomatic rate for EV-A71 is 71.4% (68.3%-74.3%) for ages 1-4, the years of greatest incidence.
Conclusion: Despite the high incidence rate of HFMD, total DALY due to HFMD is limited in comparison to other endemic diseases in the region, such as dengue and upper respiratory tract infection. With the majority of DALY caused by years of life lost, it is possible to mitigate most with increased EV-A71 vaccine coverage.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Mathematical Modelling; Other Infection, Disease, Disorder, Or Injury; Paediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
