Human LINE-1 retrotransposition requires a metastable coiled coil and a positively charged N-terminus in L1ORF1p
- PMID: 29565245
- PMCID: PMC5940361
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.34960
Human LINE-1 retrotransposition requires a metastable coiled coil and a positively charged N-terminus in L1ORF1p
Abstract
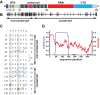
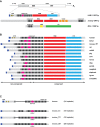
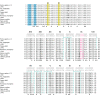
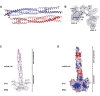
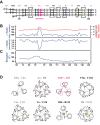
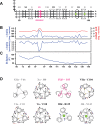
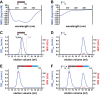
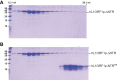
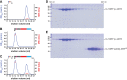
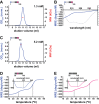
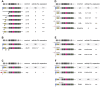
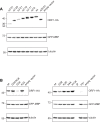
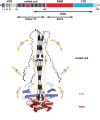
LINE-1 (L1) is an autonomous retrotransposon, which acted throughout mammalian evolution and keeps contributing to human genotypic diversity, genetic disease and cancer. L1 encodes two essential proteins: L1ORF1p, a unique RNA-binding protein, and L1ORF2p, an endonuclease and reverse transcriptase. L1ORF1p contains an essential, but rapidly evolving N-terminal portion, homo-trimerizes via a coiled coil and packages L1RNA into large assemblies. Here, we determined crystal structures of the entire coiled coil domain of human L1ORF1p. We show that retrotransposition requires a non-ideal and metastable coiled coil structure, and a strongly basic L1ORF1p amino terminus. Human L1ORF1p therefore emerges as a highly calibrated molecular machine, sensitive to mutation but functional in different hosts. Our analysis rationalizes the locally rapid L1ORF1p sequence evolution and reveals striking mechanistic parallels to coiled coil-containing membrane fusion proteins. It also suggests how trimeric L1ORF1p could form larger meshworks and indicates critical novel steps in L1 retrotransposition.
Keywords: LINE; chromosomes; coiled coil; conformational dynamics; gene expression; human; mobile DNA; molecular biophysics; structural biology.
© 2018, Khazina et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EK No competing interests declared, OW Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trimeric structure and flexibility of the L1ORF1 protein in human L1 retrotransposition.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Aug 7;18(9):1006-14. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2097. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21822284
-
Robust expression of LINE-1 retrotransposon encoded proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 27;21(1):628. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08174-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34044801 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptic genetic variation enhances primate L1 retrotransposon survival by enlarging the functional coiled coil sequence space of ORF1p.PLoS Genet. 2020 Aug 14;16(8):e1008991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008991. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32797042 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-nucleic acid interactions of LINE-1 ORF1p.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Feb;86:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.019. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29596909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated structural biology to unravel molecular mechanisms of protein-RNA recognition.Methods. 2017 Apr 15;118-119:119-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28315749 Review.
Cited by
-
LINE-1 mRNA 3' end dynamics shape its biology and retrotransposition potential.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 12;52(6):3327-3345. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1251. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38197223 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic retrotransposition in the developing rhesus macaque brain.Genome Res. 2022 Jul;32(7):1298-1314. doi: 10.1101/gr.276451.121. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 35728967 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse single-stranded nucleic acid binding proteins enable both stable protection and rapid exchange required for biological function.QRB Discov. 2025 Jan 14;6:e1. doi: 10.1017/qrd.2024.21. eCollection 2025. QRB Discov. 2025. PMID: 39944884 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of L1 retrotransposons in granulocytes from patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus.Mob DNA. 2023 May 10;14(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13100-023-00293-7. Mob DNA. 2023. PMID: 37165451 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of the Periodicity in Proteins with Coiled-Coil Structure-Enumerating All Decompositions of Sequence Periods.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8692. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158692. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955828 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

