Bioactive Peptides from Cartilage Protein Hydrolysate of Spotless Smoothhound and Their Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
- PMID: 29565311
- PMCID: PMC5923387
- DOI: 10.3390/md16040100
Bioactive Peptides from Cartilage Protein Hydrolysate of Spotless Smoothhound and Their Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
Abstract
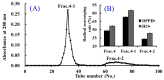
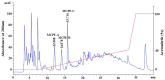
In the experiment, crude proteins from spotless smoothhound (Mustelus griseus), cartilages were isolated by HCl-Guanidine buffer, and its hydrolysate was prepared using trypsin at pH 8.0, 40 °C with a total enzyme dose of 2.5%. Subsequently, three antioxidant peptides were purified from the hydrolysate using membrane ultrafiltration, anion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, and reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography. The amino acid sequences of isolated peptides were identified as Gly-Ala-Glu-Arg-Pro (MCPE-A); Gly-Glu-Arg-Glu-Ala-Asn-Val-Met (MCPE-B); and Ala-Glu-Val-Gly (MCPE-C) with molecular weights of 528.57, 905.00, and 374.40 Da, respectively, using protein amino acid sequence analyzer and mass spectrum. MCPE-A, MCPE-B and MCPE-C exhibited good scavenging activities on 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals (DPPH•) (EC50 3.73, 1.87, and 2.30 mg/mL, respectively), hydroxyl radicals (HO•) (EC50 0.25, 0.34, and 0.06 mg/mL, respectively), 2,2'-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid radicals (ABTS⁺•) (EC50 0.10, 0.05, and 0.07 mg/mL, respectively) and superoxide anion radicals ( O 2 - •) (EC50 0.09, 0.33, and 0.18 mg/mL, respectively). MCPE-B showed similar inhibiting ability on lipid peroxidation with butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) in a linoleic acid model system. Furthermore, MCPE-A, MCPE-B, and MCPE-C could protect H₂O₂-induced HepG2 cells from oxidative stress by decreasing the content of malonaldehyde (MDA) and increasing the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and glutathione reductase (GSH-Rx). Glu, Gly, Met, and Pro in their sequences and low molecular weight could be attributed to the antioxidant activities of three isolated peptides. These results suggested that GAERP (MCPE-A), GEREANVM (MCPE-B), and AEVG (MCPE-C) from cartilage protein hydrolysate of spotless smoothhound might serve as potential antioxidants and be used in the pharmaceutical and health food industries.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; antioxidant enzyme; cartilage; peptide; protein hydrolysate; spotless smoothhound (Mustelus griseus).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Preparation, Identification, and Activity Evaluation of Eight Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Hairtail (Trichiurus japonicas) Muscle.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jan 2;17(1):23. doi: 10.3390/md17010023. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30609694 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Identification of Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Scalloped Hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini) Cartilage.Mar Drugs. 2017 Mar 1;15(3):61. doi: 10.3390/md15030061. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28257057 Free PMC article.
-
Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 3;17(5):263. doi: 10.3390/md17050263. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31058809 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional properties of food protein-derived antioxidant peptides.J Food Biochem. 2019 Jan;43(1):e12761. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12761. Epub 2019 Jan 7. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353492 Review.
-
Marine bioactive peptides as potential antioxidants.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013 May;14(3):189-98. doi: 10.2174/13892037113149990041. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013. PMID: 23721315 Review.
Cited by
-
Encapsulation of Salmon Peptides in Marine Liposomes: Physico-Chemical Properties, Antiradical Activities and Biocompatibility Assays.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 31;20(4):249. doi: 10.3390/md20040249. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447922 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, Identification, and Activity Evaluation of Eight Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Hairtail (Trichiurus japonicas) Muscle.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jan 2;17(1):23. doi: 10.3390/md17010023. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30609694 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Clinical Aspects of Bioactive Peptides from Marine Animals.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 22;11(5):1021. doi: 10.3390/antiox11051021. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antioxidant Effects of Trypsin-Hydrolysate Derived from Abalone Viscera and Fishery By-Products, and the Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity of Its Purified Bioactive Peptides.Mar Drugs. 2024 Oct 7;22(10):461. doi: 10.3390/md22100461. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452868 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Bioactive Peptides-An Overview of Generation, Structure and Application with a Focus on Food Sources.Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 13;18(8):424. doi: 10.3390/md18080424. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32823602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sila A., Bougatef A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems: A review. J. Funct. Foods. 2016;21:10–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.11.007. - DOI
-
- Guo P., Qi Y., Zhu C., Wang Q. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from Chinese cherry (Prunus pseudocerasus Lindl.) seeds. J. Funct. Foods. 2015;19:394–403. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.09.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

