Dependency of image quality on acquisition protocol and image processing in chest tomosynthesis-a visual grading study based on clinical data
- PMID: 29565673
- PMCID: PMC6221780
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170683
Dependency of image quality on acquisition protocol and image processing in chest tomosynthesis-a visual grading study based on clinical data
Abstract
Objective: To compare the quality of images obtained with two different protocols with different acquisition time and the influence from image post processing in a chest digital tomosynthesis (DTS) system.
Methods: 20 patients with suspected lung cancer were imaged with a chest X-ray equipment with tomosynthesis option. Two examination protocols with different acquisition times (6.3 and 12 s) were performed on each patient. Both protocols were presented with two different image post-processing (standard DTS processing and more advanced processing optimised for chest radiography). Thus, 4 series from each patient, altogether 80 series, were presented anonymously and in a random order. Five observers rated the quality of the reconstructed section images according to predefined quality criteria in three different classes. Visual grading characteristics (VGC) was used to analyse the data and the area under the VGC curve (AUCVGC) was used as figure-of-merit. The 12 s protocol and the standard DTS processing were used as references in the analyses.
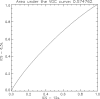
Results: The protocol with 6.3 s acquisition time had a statistically significant advantage over the vendor-recommended protocol with 12 s acquisition time for the classes of criteria, Demarcation (AUCVGC = 0.56, p = 0.009) and Disturbance (AUCVGC = 0.58, p < 0.001). A similar value of AUCVGC was found also for the class Structure (definition of bone structures in the spine) (0.56) but it could not be statistically separated from 0.5 (p = 0.21). For the image processing, the VGC analysis showed a small but statistically significant advantage for the standard DTS processing over the more advanced processing for the classes of criteria Demarcation (AUCVGC = 0.45, p = 0.017) and Disturbance (AUCVGC = 0.43, p = 0.005). A similar value of AUCVGC was found also for the class Structure (0.46), but it could not be statistically separated from 0.5 (p = 0.31).
Conclusion: The study indicates that the protocol with 6.3 s acquisition time yields slightly better image quality than the vender-recommended protocol with acquisition time 12 s for several anatomical structures. Furthermore, the standard gradation processing (the vendor-recommended post-processing for DTS), yields to some extent advantage over the gradation processing/multiobjective frequency processing/flexible noise control processing in terms of image quality for all classes of criteria. Advances in knowledge: The study proves that the image quality may be strongly affected by the selection of DTS protocol and that the vendor-recommended protocol may not always be the optimal choice.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

