Expression, Distribution, and Role of C-Type Lectin Receptors in the Human and Animal Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube: A Review
- PMID: 29565818
- PMCID: PMC6017961
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23040734
Expression, Distribution, and Role of C-Type Lectin Receptors in the Human and Animal Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube: A Review
Abstract
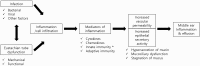
Otitis media (OM) is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear (ME), regardless of cause or pathological mechanism. Among the molecular biological studies assessing the pathology of OM are investigations into the expression of C-type lectin receptors (CLR) in the ME and Eustachian tube (ET). To date, nine studies have evaluated CLR expression in the ME and ET. The expression of individual CLRs in mammalian ME and ET varies by species and model of OM. Assessments have shown that the patterns of CLR expression in the ME and ET vary; that CLR expression may vary by type of OM; and that the distribution and levels of expression of CLRs may depend on the presence or absence of inflammation, with variations even within the same species and same tissue. Infection of the ME and ET with various pathogens is a common cause of all types of OM, with host responses to pathogens mediated initially by the innate immune system. CLRs are important factors in the innate immune system because they act as both adhesion molecules and as pathogen recognition receptors. The expression of CLRs in OM tissues suggests that CLRs are associated with the pathogenesis of various types of OM.
Keywords: c-type lectin receptor; glycans; human middle ear; lectin; otitis media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review: Expression of Aquaporins in Otitis Media.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 17;18(10):2164. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102164. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29039751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of C-type lectin receptor mRNA in otitis media with effusion and chronic otitis media with and without cholesteatoma.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019 Oct;46(5):672-680. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.12.011. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019. PMID: 30609964
-
Otitis media in sperm-associated antigen 6 (Spag6)-deficient mice.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112879. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393619 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study indicates novel associations of annexin A13 to secretory and GAS2L2 with mucous otitis media.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 7;14(1):18344. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68781-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39112560 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid C-type lectin receptors in host-pathogen interactions and glycan-based targeting.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2024 Oct;82:102521. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102521. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39214069 Review.
Cited by
-
Mannose and Lactobionic Acid in Nasal Vaccination: Enhancing Antigen Delivery via C-Type Lectin Receptors.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 8;16(10):1308. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101308. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The matrisome landscape controlling in vivo germ cell fates.Nat Commun. 2024 May 17;15(1):4200. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48283-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38760342 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in targeted delivery of mRNA into immune cells for enhanced cancer therapy.Theranostics. 2024 Sep 3;14(14):5528-5550. doi: 10.7150/thno.93745. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39310113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Role of Rabbit Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-2 (NOD2)-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Resistance to Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 26;8:220. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00220. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29998088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bluestone C.D., Klein J.O. Otitis media and eustachian tube dysfunction. In: Bluestone C.D., Stool S.E., Alper C.M., editors. Pediatric Otolaryngology. 4th ed. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2003. pp. 474–685.
-
- Paparella M.M., Kim C.S., Goycoolea M.V., Giebink S. Pathogenesis of otits media. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1977;86:481–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical