An unfavorable body composition is common in early arthritis patients: A case control study
- PMID: 29565986
- PMCID: PMC5863963
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193377
An unfavorable body composition is common in early arthritis patients: A case control study
Abstract
Background: An unfavorable body composition is often present in chronic arthritis patients. This unfavorable composition is a loss of muscle mass, with a stable or increased (abdominal) fat mass. Since it is unknown when this unfavorable composition develops, we compared body composition in disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD)-naive early arthritis patients with non-arthritis controls and explored the association, in early arthritis patients, with disease activity and traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: 317 consecutive early arthritis patients (84% rheumatoid arthritis according to 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria) and 1268 age-/gender-/ethnicity-matched non-arthritis controls underwent a Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan to assess fat percentage, fat mass index, fat mass distribution and appendicular lean (muscle) mass index. Additionally, disease activity, health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), acute phase proteins, lipid profile and blood pressure were evaluated.
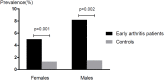
Results: Loss of muscle mass (corrected for age suspected muscle mass) was 4-5 times more common in early arthritis patients, with a significantly lower mean appendicular lean mass index (females 6% and males 7% lower, p<0.01). Patients had more fat distributed to the trunk (females p<0.01, males p = 0.07) and females had a 4% higher mean fat mass index (p<0.01). An unfavorable body composition was associated with a higher blood pressure and an atherogenic lipid profile. There was no relationship with disease activity, HAQ or acute phase proteins.
Conclusion: Loss of muscle mass is 4-5 times more common in early arthritis patients, and is in early arthritis patients associated with a higher blood pressure and an atherogenic lipid profile. Therefore, cardiovascular risk is already increased at the clinical onset of arthritis making cardiovascular risk management necessary in early arthritis patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in body composition and metabolic profile during interleukin 6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017 Aug;8(4):639-646. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12189. Epub 2017 Mar 18. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017. PMID: 28316139 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Low Lean Mass in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross- Sectional Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Nov 8;55(11):730. doi: 10.3390/medicina55110730. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31717450 Free PMC article.
-
Association of body composition with disability in rheumatoid arthritis: impact of appendicular fat and lean tissue mass.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Oct 15;59(10):1407-15. doi: 10.1002/art.24109. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18821641 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of abdominal adiposity and body composition with endothelial dysfunction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;33(4):516-23. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26148347
-
Sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, influence of disease activity and associated factors.Rheumatol Int. 2017 Jun;37(6):1015-1020. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3665-x. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Rheumatol Int. 2017. PMID: 28258473
Cited by
-
Distinction and prognosis of early arthritis phenotypes: an analysis in three European cohorts.RMD Open. 2023 Nov;9(4):e003611. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003611. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37914180 Free PMC article.
-
Is rheumatoid arthritis always preceded by a symptomatic at-risk phase of arthralgia?RMD Open. 2024 Nov 12;10(4):e004714. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004714. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 39537206 Free PMC article.
-
eDRAM: Effective early disease risk assessment with matrix factorization on a large-scale medical database: A case study on rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 26;13(11):e0207579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207579. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30475847 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Deal with Rheumatoid Cachexia: Prevalence, Diagnostic Criteria, Treatment Effects and Evidence for Management.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022 Sep 30;33(3):271-290. doi: 10.31138/mjr.33.3.271. eCollection 2022 Sep. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36531417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of TNF and Non-TNF-Targeted Biologics on Body Composition in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 29;10(3):487. doi: 10.3390/jcm10030487. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33573047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun J, Kruger K, Manger B, Schneider M, Specker C, Trappe HJ. Cardiovascular Comorbidity in Inflammatory Rheumatological Conditions. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2017;114:197–203. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0197 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nurmohamed MT, Heslinga M, Kitas GD. Cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2015;11:693–704. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.112 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holmqvist ME, Wedren S, Jacobsson LT, Klareskog L, Nyberg F, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, et al. Rapid increase in myocardial infarction risk following diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis amongst patients diagnosed between 1995 and 2006. J Intern Med 2010;268:578–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02260.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Innala L, Moller B, Ljung L, Magnusson S, Smedby T, Sodergren A, et al. Cardiovascular events in early RA are a result of inflammatory burden and traditional risk factors: a five year prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther 2011;13:R131 doi: 10.1186/ar3442 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kerola AM, Kauppi MJ, Kerola T, Nieminen TV. How early in the course of rheumatoid arthritis does the excess cardiovascular risk appear? Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1606–15. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201334 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical