Development of Tizanidine HCl-Meloxicam loaded mucoadhesive buccal films: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation
- PMID: 29566073
- PMCID: PMC5864138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194410
Development of Tizanidine HCl-Meloxicam loaded mucoadhesive buccal films: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation
Abstract
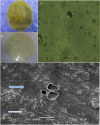
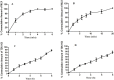
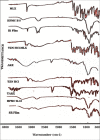
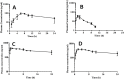
The purpose of the study was to develop Tizanidine HCl (TZN) and Meloxicam (MLX) loaded bilayer mucoadhesive films intended for buccal administration, aiming to enhance the bioavailability. Bilayer films were prepared by solvent evaporation technique selecting arabinoxylan (ARX) as a sustained release (SR) layer forming polymer and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) E-15 as an immediate release (IR) layer-forming polymer. Prepared films were subjected to in-vitro drug release, surface morphology, mechanical strength, compatibility of the ingredients, drug contents, ex-vivo mucoadhesion strength and drug permeation. Crossover study design was applied to study the in-vivo pharmacokinetics by using albino rabbits. Various pharmacokinetic parameters including AUC, Cmax, tmax and t1/2 of both drugs loaded in films were compared with standard solution/dispersion administered to the rabbits at the dose of 1mg/kg. The results unveiled instant release and permeation of MLX from IR layer, while good controlled release and permeation characteristics of TZN from SR films over 8 h. films were of uniform thickness with smooth surface and satisfactory mechanical strength. Mucoadhesion strength was sufficient to provide suitable contact time with mucosal membrane. The pharmacokinetic study exhibited prompt absorption of MLX with better AUC 0-t (6655.64 ng/ml*h vs 6538.99 ng/ml*h) and Cmax (436.98 ng/ml vs 411.33 ng/ml) from oral dispersion. Similarly buccal films has shown enhanced half-life (9.91hr vs 2.51 hr), AUC 0-t (1043.4 ng/ml*h vs 149.1 ng/ml*h) and Cmax (91.92 ng/ml vs 42.29 ng/ml) from oral solution. A statistical investigation disclosed a significantly improved pharmacokinetics of TZN and MLX after their absorption across buccal route following administration of buccal film (p<0.05). ARX proved expedient and bilayer buccal films as a drug delivery system ascertained the dual effect of providing instant release of one active agent and persistent release of another one with improved pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thiolation of arabinoxylan and its application in the fabrication of controlled release mucoadhesive oral films.Daru. 2017 Mar 20;25(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s40199-017-0172-2. Daru. 2017. PMID: 28320456 Free PMC article.
-
Development of thiomer based buccal films for the enhancement of bioavailability: An in-vivo analysis.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019 Mar;32(2 (Supplementary)):759-764. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31103968
-
Development and evaluation of buccal films impregnated with selegiline-loaded nanospheres.Drug Deliv. 2016 Sep;23(7):2154-2162. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.948644. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 25182182
-
Overview and Future Potential of Buccal Mucoadhesive Films as Drug Delivery Systems for Biologics.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Jan 1;18(1):3-14. doi: 10.1208/s12249-016-0525-z. Epub 2016 Apr 15. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 27084567 Review.
-
Manufacture and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Feb;77(2):187-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.023. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21130875 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterial-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Pain Treatment and Relief: From the Delivery of a Single Drug to Co-Delivery of Multiple Therapeutics.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 13;15(9):2309. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092309. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statistically Optimized Polymeric Buccal Films of Eletriptan Hydrobromide and Itopride Hydrochloride: An In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1551. doi: 10.3390/ph16111551. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004417 Free PMC article.
-
Tizanidine: Advances in Pharmacology & Therapeutics and Drug Formulations.J Pain Res. 2024 Mar 21;17:1257-1271. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S461032. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38529017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight into Preparatory Methods and Characterization of Orodispersible Film-A Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 9;15(7):844. doi: 10.3390/ph15070844. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucoadhesive buccal film of almotriptan improved therapeutic delivery in rabbit model.Saudi Pharm J. 2020 Feb;28(2):201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.022. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Saudi Pharm J. 2020. PMID: 32042259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ketul P, Patel K, Patel M, Patel N (2013) Fast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach to Oral Drug Delivery. International Journal of Pharmacy Teaching & Practices (IJPTP) 4.
-
- Bahri-Najafi GK, Yazdanian ER (2012) Formulation and evaluation of triamcinolon acetonid bilayer buccal adhesive film. Research in pharmaceutical sciences 7: S343.
-
- Kumar R, Sulochana M (2014) Fat Dissolving Films: A Unique Strategy for Drug Delivery. Asian J Pharmaceut Res 4: 47–55.
-
- Jay S, Fountain W, Cui Z, Mumper RJ (2002) Transmucosal delivery of testosterone in rabbits using novel bi‐layer mucoadhesive wax‐film composite disks. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 91: 2016–2025. doi: 10.1002/jps.10198 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jain NK, Kulkarni SK, Singh A (2002) Modulation of NSAID-induced antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects by α2-adrenoceptor agonists with gastroprotective effects. Life sciences 70: 2857–2869. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

