Patterns of sensitization to inhalant and food allergens among pediatric patients from the Moscow region (Russian Federation)
- PMID: 29566093
- PMCID: PMC5864043
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194775
Patterns of sensitization to inhalant and food allergens among pediatric patients from the Moscow region (Russian Federation)
Abstract
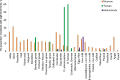
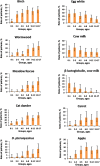
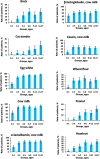
The immunological profiles of human specific IgE (sIgE) and specific IgG4 (sIgG4) vary by genetic predisposition, living conditions in different geographical locations and patient's age. The aim of our study was to analyze sIgE and sIgG4 patterns and their age-dependent changes in patients from the Moscow region. For identifying sIgE and sIgG4 profiles the blood samples from 513 patients aged 6 months to 17 years who were showing symptoms of allergic diseases were analyzed using microarrays containing 31 allergens. The highest sIgE prevalence was observed for birch pollen (32%) among pollen allergens, cat dander (24%) among indoor allergens, and egg whites (21%) among food allergens. The most common sIgG4 response was developed toward egg whites (80% of patients). Age-related elevation was identified for patients with increased sIgE to pollen allergens and indoor allergens (cat or dog dander and house dust mites). For each allergen, the proportion of cases with significant levels of sIgG4 appeared to increase with patients' age. The data on allergen-specific sIgE and sIgG4 prevalence show both general trends and some local special aspects that are indicative for the Moscow region. This information should be useful in terms of epidemiology of allergic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allergen-specific IgE and IgG4 patterns among patients with different allergic diseases.World Allergy Organ J. 2018 Dec 3;11(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40413-018-0220-5. eCollection 2018. World Allergy Organ J. 2018. PMID: 30524646 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of the sensitization characteristics and changes trend of common allergens in a hospital of pediatric in Beijing City from 2019 to 2023].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 6;58(12):1894-1901. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20240701-00524. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39710467 Chinese.
-
Analysis of allergens in 5 473 patients with allergic diseases in Harbin, China.Biomed Environ Sci. 2013 Nov;26(11):886-93. doi: 10.3967/bes2013.017. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013. PMID: 24331533
-
The impact of allergy on atopic eczema from data from epidemiological studies.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;8(5):418-22. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32830e71a7. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18769194 Review.
-
Prevention of allergic disease in childhood: clinical and epidemiological aspects of primary and secondary allergy prevention.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004 Jun;15 Suppl 16:4-5, 9-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2004.0148b.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15125698 Review.
Cited by
-
Cluster Analysis of Inhalant Allergens in South Korea: A Computational Model of Allergic Sensitization.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Feb;14(1):93-99. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.01921. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32623852 Free PMC article.
-
Allergies to Allergens from Cats and Dogs: A Review and Update on Sources, Pathogenesis, and Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10520. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910520. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The EIMB Hydrogel Microarray Technology: Thirty Years Later.Acta Naturae. 2018 Oct-Dec;10(4):4-18. Acta Naturae. 2018. PMID: 30713758 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic sensitization among Danish infants at 13 months of age.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2019 Sep;7(3):183-190. doi: 10.1002/iid3.260. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2019. PMID: 31190476 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Allergen-specific IgE and IgG4 patterns among patients with different allergic diseases.World Allergy Organ J. 2018 Dec 3;11(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40413-018-0220-5. eCollection 2018. World Allergy Organ J. 2018. PMID: 30524646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burks AW, Tang M, Sicherer S, Muraro A, Eigenmann PA, Ebisawa M et al. ICON: food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:906–920. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartůnková J, Kayserová J, Shoenfeld Y. Allergy and autoimmunity: parallels and dissimilarity: the yin and yang of immunopathology. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:302‒308. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2008.09.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van de Veen W, Akdis M. Role of IgG4 in IgE-mediated allergic responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:1434–1435. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vazquez-Ortiz M, Pascal M, Jiménez-Feijoo R, Lozano J, Giner MT, Alsina L et al. Ovalbumin-specific IgE/IgG4 ratio might improve the prediction of cooked and uncooked egg tolerance development in egg-allergic children. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;44:579–588. doi: 10.1111/cea.12273 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

