Efficacy and Safety of First-line Avelumab Treatment in Patients With Stage IV Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Preplanned Interim Analysis of a Clinical Trial
- PMID: 29566106
- PMCID: PMC5885245
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0077
Efficacy and Safety of First-line Avelumab Treatment in Patients With Stage IV Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Preplanned Interim Analysis of a Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer that is associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with distant metastatic disease. Results of part A of the JAVELIN Merkel 200 trial (avelumab in patients with Merkel cell carcinoma) showed that avelumab, an anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody, demonstrated efficacy in second-line or later treatment of patients with metastatic MCC (mMCC).
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of avelumab as first-line treatment for patients with distant mMCC.
Design, setting, and participants: JAVELIN Merkel 200 part B is an international, multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trial of first-line avelumab monotherapy. Eligible patients were adults with mMCC who had not received prior systemic treatment for metastatic disease. Patients were not selected for PD-L1 expression or Merkel cell polyomavirus status. Data were collected from April 15, 2016, to March 24, 2017, and enrollment is ongoing.
Interventions: Patients received avelumab, 10 mg/kg, by 1-hour intravenous infusion every 2 weeks until confirmed disease progression, unacceptable toxic effects, or withdrawal occurred.
Main outcomes and measures: Tumor status was assessed every 6 weeks and evaluated by independent review committee per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1. The primary end point was durable response, defined as an objective response with a duration of at least 6 months. Secondary end points include best overall response, duration of response, progression-free survival, safety, and tolerability.
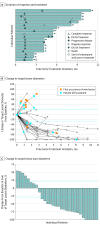
Results: As of March 24, 2017, 39 patients were enrolled (30 men and 9 women; median age, 75 years [range, 47-88 years]), with a median follow-up of 5.1 months (range, 0.3-11.3 months). In a preplanned analysis, efficacy was assessed in 29 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up; the confirmed objective response rate was 62.1% (95% CI, 42.3%-79.3%), with 14 of 18 responses (77.8%) ongoing at the time of analysis. In responding patients, the estimated proportion with duration of response of at least 3 months was 93% (95% CI, 61%-99%); duration of response of at least 6 months, 83% (95% CI, 46%-96%). First-line avelumab treatment was generally well tolerated, and no treatment-related deaths or grade 4 adverse events occurred.
Conclusions and relevance: High rates of response to first-line avelumab therapy in patients with distant mMCC build on previously reported antitumor activity after second-line or later treatment, and maturing progression-free survival data suggest that responses are durable. These data further support avelumab's approval in the United States and European Union and use as a standard-of-care treatment for mMCC.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02155647.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Updated efficacy of avelumab in patients with previously treated metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma after ≥1 year of follow-up: JAVELIN Merkel 200, a phase 2 clinical trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Jan 19;6(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0310-x. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29347993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab in patients with previously treated metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma: long-term data and biomarker analyses from the single-arm phase 2 JAVELIN Merkel 200 trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 May;8(1):e000674. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000674. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32414862 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma: a multicentre, single-group, open-label, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Oct;17(10):1374-1385. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30364-3. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27592805 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab: A Review in Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Target Oncol. 2018 Jun;13(3):409-416. doi: 10.1007/s11523-018-0571-4. Target Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29799096 Review.
-
PD-L1 inhibition with avelumab for metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;11(4):345-359. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1445966. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29478343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Related Uncommon Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 29;12(9):2091. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092091. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
13-year survival oligometastatic Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Sep 18;18(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04750-6. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39289742 Free PMC article.
-
Successful immunotherapy and irradiation in a HIV-positive patient with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2018 Dec 31;15:42-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2018.12.004. eCollection 2019 Feb. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30671549 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma of the eyelid and periocular region: A review.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr 18;35(3):186-192. doi: 10.4103/SJOPT.SJOPT_55_21. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35601863 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma.Skin Health Dis. 2021 Jun 16;1(4):e55. doi: 10.1002/ski2.55. eCollection 2021 Dec. Skin Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 35663768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schadendorf D, Lebbé C, Zur Hausen A, et al. . Merkel cell carcinoma: epidemiology, prognosis, therapy and unmet medical needs. Eur J Cancer. 2017;71:-. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Merkel Cell Carcinoma, version 1. https://www.nccn.org/store/login/login.aspx?ReturnURL=https://www.nccn.o.... Updated 2017. Accessed October 19, 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cowey CL, Mahnke L, Espirito J, Helwig C, Oksen D, Bharmal M. Real-world treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma treated with chemotherapy in the USA. Future Oncol. 2017;13(19):1699-1710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

