Cognitive-behavioural interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults
- PMID: 29566425
- PMCID: PMC6494390
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010840.pub2
Cognitive-behavioural interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults
Abstract
Background: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a developmental condition characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity, along with deficits in executive function, emotional regulation and motivation. The persistence of ADHD in adulthood is a serious clinical problem.ADHD significantly affects social interactions, study and employment performance.Previous studies suggest that cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) could be effective in treating adults with ADHD, especially when combined with pharmacological treatment. CBT aims to change the thoughts and behaviours that reinforce harmful effects of the disorder by teaching people techniques to control the core symptoms. CBT also aims to help people cope with emotions, such as anxiety and depression, and to improve self-esteem.
Objectives: To assess the effects of cognitive-behavioural-based therapy for ADHD in adults.
Search methods: In June 2017, we searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, seven other databases and three trials registries. We also checked reference lists, handsearched congress abstracts, and contacted experts and researchers in the field.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating any form of CBT for adults with ADHD, either as a monotherapy or in conjunction with another treatment, versus one of the following: unspecific control conditions (comprising supportive psychotherapies, no treatment or waiting list) or other specific interventions.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard methodological procedures suggested by Cochrane.
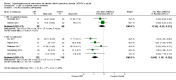
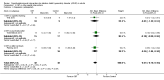
Main results: We included 14 RCTs (700 participants), 13 of which were conducted in the northern hemisphere and 1 in Australia.Primary outcomes: ADHD symptomsCBT versus unspecific control conditions (supportive psychotherapies, waiting list or no treatment)- CBT versus supportive psychotherapies: CBT was more effective than supportive therapy for improving clinician-reported ADHD symptoms (1 study, 81 participants; low-quality evidence) but not for self-reported ADHD symptoms (SMD -0.16, 95% CI -0.52 to 0.19; 2 studies, 122 participants; low-quality evidence; small effect size).- CBT versus waiting list: CBT led to a larger benefit in clinician-reported ADHD symptoms (SMD -1.22, 95% CI -2.03 to -0.41; 2 studies, 126 participants; very low-quality evidence; large effect size). We also found significant differences in favour of CBT for self-reported ADHD symptoms (SMD -0.84, 95% CI -1.18 to -0.50; 5 studies, 251 participants; moderate-quality evidence; large effect size).CBT plus pharmacotherapy versus pharmacotherapy alone: CBT with pharmacotherapy was more effective than pharmacotherapy alone for clinician-reported core symptoms (SMD -0.80, 95% CI -1.31 to -0.30; 2 studies, 65 participants; very low-quality evidence; large effect size), self-reported core symptoms (MD -7.42 points, 95% CI -11.63 points to -3.22 points; 2 studies, 66 participants low-quality evidence) and self-reported inattention (1 study, 35 participants).CBT versus other interventions that included therapeutic ingredients specifically targeted to ADHD: we found a significant difference in favour of CBT for clinician-reported ADHD symptoms (SMD -0.58, 95% CI -0.98 to -0.17; 2 studies, 97 participants; low-quality evidence; moderate effect size) and for self-reported ADHD symptom severity (SMD -0.44, 95% CI -0.88 to -0.01; 4 studies, 156 participants; low-quality evidence; small effect size).Secondary outcomesCBT versus unspecific control conditions: we found differences in favour of CBT compared with waiting-list control for self-reported depression (SMD -0.36, 95% CI -0.60 to -0.11; 5 studies, 258 participants; small effect size) and for self-reported anxiety (SMD -0.45, 95% CI -0.71 to -0.19; 4 studies, 239 participants; small effect size). We also observed differences in favour of CBT for self-reported state anger (1 study, 43 participants) and self-reported self-esteem (1 study 43 participants) compared to waiting list. We found no differences between CBT and supportive therapy (1 study, 81 participants) for self-rated depression, clinician-rated anxiety or self-rated self-esteem. Additionally, there were no differences between CBT and the waiting list for self-reported trait anger (1 study, 43 participants) or self-reported quality of life (SMD 0.21, 95% CI -0.29 to 0.71; 2 studies, 64 participants; small effect size).CBT plus pharmacotherapy versus pharmacotherapy alone: we found differences in favour of CBT plus pharmacotherapy for the Clinical Global Impression score (MD -0.75 points, 95% CI -1.21 points to -0.30 points; 2 studies, 65 participants), self-reported depression (MD -6.09 points, 95% CI -9.55 points to -2.63 points; 2 studies, 66 participants) and self-reported anxiety (SMD -0.58, 95% CI -1.08 to -0.08; 2 studies, 66 participants; moderate effect size). We also observed differences favouring CBT plus pharmacotherapy (1 study, 31 participants) for clinician-reported depression and clinician-reported anxiety.CBT versus other specific interventions: we found no differences for any of the secondary outcomes, such as self-reported depression and anxiety, and findings on self-reported quality of life varied across different studies.
Authors' conclusions: There is low-quality evidence that cognitive-behavioural-based treatments may be beneficial for treating adults with ADHD in the short term. Reductions in core symptoms of ADHD were fairly consistent across the different comparisons: in CBT plus pharmacotherapy versus pharmacotherapy alone and in CBT versus waiting list. There is low-quality evidence that CBT may also improve common secondary disturbances in adults with ADHD, such as depression and anxiety. However, the paucity of long-term follow-up data, the heterogeneous nature of the measured outcomes, and the limited geographical location (northern hemisphere and Australia) limit the generalisability of the results. None of the included studies reported severe adverse events, but five participants receiving different modalities of CBT described some type of adverse event, such as distress and anxiety.
Conflict of interest statement
Pablo Luis Lopez ‐ none known. Fernando Manuel Torrente ‐ none known. Agustín Ciapponi ‐ none known. Alicia Graciela Lischinsky received payment as an invited speaker at Ely Lilly and Jannsen Cilag Labs. Marcelo Cetkovich‐Bakmas ‐ none known. Juan Ignacio Rojas ‐ none known. Marina Romano received payment from Novartis Argentina for review preparation and funds for travel/accommodation/meeting expenses from Boehringer‐Ingelheim. MR declares no conflict of interest related to this review. Facundo F Manes ‐ none known.
Figures
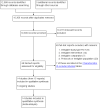

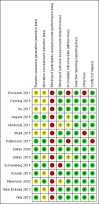






























Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010840
References
References to studies included in this review
Emilsson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Emilsson B, Gudjonsson G, Sigurdsson JF, Baldursson G, Einarsson E, Olafsdottir H, et al. Cognitive behaviour therapy in medication‐treated adults with ADHD and persistent symptoms: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry 2011;11:116. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-11-116; ACTRN12611000533998; PMC3155481; PUBMED: 21787431] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Fleming 2015 {published data only}
Gu 2017 {published data only}
Hepark 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hepark S, Janssen L, Vries A, Schoenberg PLA, Donders R, Kan CC, et al. The efficacy of adapted MBCT on core symptoms and executive functioning in adults with ADHD: a preliminary randomized controlled trial. Journal of Attention Disorders 2015 Nov 20 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1177/1087054715613587; PUBMED: 26588940] - DOI - PubMed
Hirvikoski 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hirvikoski T, Waaler E, Alfredsson J, Pihlgren C, Holmström A, Johnson A, et al. Reduced ADHD symptoms in adults with ADHD after structured skills training group: results from a randomized controlled trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2011;49(3):175‐85. [DOI: 10.1016/j.brat.2011.01.001; PUBMED: 21295767] - DOI - PubMed
Moëll 2015 {published data only}
-
- Moëll B, Kollberg L, Nasri B, Lindefors N, Kaldo V. Living SMART – A randomized controlled trial of a guided online course teaching adults with ADHD or sub‐clinical ADHD to use smartphones to structure their everyday life. Internet Interventions 2015;2(1):24‐31. [DOI: 10.1016/j.invent.2014.11.004] - DOI
Pettersson 2017 {published data only}
Safren 2005 {published data only}
Safren 2010 {published data only}
-
- Safren SA, Sprich S, Mimiaga MJ, Surman C, Knouse L, Groves M, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy vs relaxation with educational support for medication‐treated adults with ADHD and persistent symptoms: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010;304(8):875‐80. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2010.1192; NCT00118911; PMC3641654; PUBMED: 20736471] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schoenberg 2014 {published data only}
-
- Schoenberg PL, Hepark S, Kan CC, Barendregt HP, Buitelaar JK, Speckens AE. Effects of mindfulness‐based cognitive therapy on neurophysiological correlates of performance monitoring in adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Neurophysiology 2014;125(7):1407‐16. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.11.031; PUBMED: 24374088] - DOI - PubMed
Solanto 2010 {published data only}
Stevenson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Stevenson CS, Stevenson RJ, Whitmont S. A self‐directed psychosocial intervention with minimal therapist contact for adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy 2003;10(2):93‐101. [DOI: 10.1002/cpp.356] - DOI
Vidal Estrada 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vidal R, Bosch R, Nogueira M, Gómez‐Barros N, Valero S, Palomar G, et al. Psychoeducation for adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder vs cognitive behavioral group therapy: a randomized controlled pilot study. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2013;201(10):894‐900. [DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0b013e3182a5c2c5; PUBMED: 24080677] - DOI - PubMed
Virta 2010 {published data only}
-
- Virta M, Salakari A, Antila M, Chydenius E, Partinen M, Kaski M, et al. Short cognitive behavioral therapy and cognitive training for adults with ADHD – a randomized controlled pilot study. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 2010;6(1):443‐53. [DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S11743; PMC2938293; PUBMED: 20856608] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cherkasova 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cherkasova MV, French LR, Syer CA, Cousins L, Galina H, Ahmadi‐Kashani Y, et al. Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy with and without medication for adults with ADHD: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Attention Disorders 2016 Oct 6 [Epub ahead of print]. [10.1177/1087054716671197] - PubMed
Mitchell 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell JT, McIntyre EM, English JS, Dennis MF, Beckham JC, Kollins SH. A pilot trial of mindfulness meditation training for ADHD in adulthood: impact on core symptoms, executive functioning,and emotion dysregulation. Journal of Attention Disorders 2017;21(13):1105‐20. [DOI: 10.1177/1087054713513328; PMC4045650; PUBMED: 4305060] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Philipsen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Philipsen A, Jans T, Graf A, Matthies S, Borel P, Colla M, et al. Effects of group psychotherapy, individual counseling, methylphenidate, and placebo in the treatment of adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015;72(12):1199‐210. [DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2146; ISRCTN54096201; PUBMED: 26536057] - DOI - PubMed
Serra‐Pla 2017 {published data only}
-
- Serra‐Pla JF, Pozuelo M, Richarte V, Corrales M, Ibáñez Pol, Bellina M, et al. Treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults using virtual reality through a mindfulness programme [Tratamiento del trastorno por déficit de atención/hiperactividad en la edad adulta a través de la realidad virtual mediante un programa de mindfulness]. Revista de Neurología 2017;64(s01):S117‐22. [PUBMED: 28256698] - PubMed
Weiss 2012 {published data only}
Young 2015 {published data only}
-
- Young S, Khondoker M, Emilsson B, Sigurdsson JF, Philipp‐Wiegmann F, Baldursson G, et al. Cognitive‐behavioural therapy in medication‐treated adults with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder and co‐morbid psychopathology: a randomized controlled trial using multi‐level analysis. Psychological Medicine 2015;45(13):2793–804. [DOI: 10.1017/S0033291715000756; PMC4595859; PUBMED: 26022103] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Young 2017 {published data only}
-
- Young S, Emilsson B, Sigurdsson JF, Khondoker M, Philipp‐Wiegmann F, Baldursson G, et al. A randomized controlled trial reporting functional outcomes of cognitive‐behavioural therapy in medication‐treated adults with ADHD and comorbid psychopathology. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2017;267(3):267‐76. [DOI: 10.1007/s00406-016-0735-0; PMC5357275] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN03732556 {published data only}
-
- Dittner AJ, Rimes KA, Russell AJ, Chalder T. Protocol for a proof of concept randomized controlled trial of cognitive‐behavioural therapy for adult ADHD as a supplement to treatment as usual, compared with treatment as usual alone. BMC Psychiatry 2014;14:248. [DOI: 10.1186/s12888-014-0248-1] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
NCT02062411 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02062411. A randomized controlled study of cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with attention deficit disorder [A randomized controlled study of cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with attention deficit disorder]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02062411 (first received 12 February 2014).
NCT02210728 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02210728. Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy in treatment of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy in treatment of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02210728 (first received 31 July 2014).
NCT02463396 {published data only}
NCT02829970 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02829970. Helping college students with ADHD lead healthier lifestyles [Behavioral activation to reduce problem alcohol use In college students with ADHD]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02829970 (first received 7 July 2016).
Additional references
Achenbach 1998
Adler 2002
-
- Adler LA, Chua HC. Management of ADHD in adults. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2002;63(Suppl 12):29‐35. [PUBMED: 12562059] - PubMed
Adler 2003
-
- Adler LA, Spencer T, Biederman J. Adult ADHD Investigator Symptom Rating Scale–AISRS. Boston (MA); New York (NY): Massachusetts General Hospital; New York University School of Medicine, 2003.
AJCD 2001
-
- America Journal of Clinical Dermatology. Cutaneous drug reaction case reports: from the world literature. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2001;2(4):267‐74. [PUBMED: 11817970] - PubMed
Amador‐Campos 2014
Antshel 2011
Atkins 2004
-
- Atkins D, Eccles M, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Henry D, Hill S, et al. Systems for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations I: critical appraisal of existing approaches The GRADE Working Group. BMC Health Services Research 2004;4(1):38. [DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-4-38; PMC545647; PUBMED: 15615589] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Barkley 1998a
-
- Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Attention‐Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Clinical Workbook. 2nd Edition. New York (NY): Guilford Press, 1998.
Barkley 1998b
-
- Barkley RA. Attention Deficit‐Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. 2nd Edition. New York (NY): Guilford Press, 1998.
Barkley 1999
-
- Barkley RA. Niños Hiperactivos: Cómo Comprender y Atender sus Necesidades Especiales. Guía Completa del Trastorno por Déficit de Atención con Hiperactividad [Hyperactive Children: How to Understand and Address their Special Needs: Complete Guide to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder]. Barcelona (ES): Paidós, 1999.
Barkley 2002
-
- Barkley RA. Major life activity and health outcomes associated with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2002;63(Suppl 12):10‐5. [PUBMED: 12562056] - PubMed
Barkley 2006a
Barkley 2006b
-
- Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Attention‐Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Clinical Workbook. 3rd Edition. New York (NY): Guilford Press, 2006.
Barkley 2008
-
- Barkley RA, Murphy KR, Fischer M. ADHD in Adults: What the Science Says. New York (NY): Guilford Press, 2008.
Barkley 2011
-
- Barkley RA. Barkley Adult ADHD Rating Scale‐IV (BAARS‐IV). New York (NY): Guilford Press, 2011.
Beck 1961
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1961;4:561‐71. [PUBMED: 13688369] - PubMed
Beck 1988
-
- Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56(6):893–7. [PUBMED: 3204199] - PubMed
Beck 1993
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Beck Anxiety Inventory Manual. San Antonio (TX): Psychological Corporation, 1993.
Beck 1996
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory‐II. San Antonio (TX): Psychological Corporation, 1996.
Beck 2012
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Järvå H. BAI – Beck Anxiety Inventory: Manual, Svensk Version. Stockholm (SE): Pearson, 2012.
Biederman 1993
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV, Spencer T, Wilens T, Norman D, Lapey KA, et al. Patterns of psychiatric comorbidity, cognition, and psychosocial functioning in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry 1993;150(12):1792‐8. [DOI: 10.1176/ajp.150.12.1792; PUBMED: 8238632] - DOI - PubMed
Biederman 2002
Biederman 2006
Brassett‐Harknett 2007
-
- Brassett‐Harknett A, Butler N. Attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an overview of the etiology and a review of the literature relating to the correlates and lifecourse outcomes for men and women. Clinical Psychology Review 2007;27(2):188‐210. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.06.001; PUBMED: 16081194] - DOI - PubMed
Brod 2005
-
- Brod M, Perwien A, Adler L, Spencer T, Johnston J. Conceptualization and assessment of quality of life for adults with attention deficit disorder. Primary Psychiatry 2005;12(6):58‐64. [www.researchgate.net/profile/Meryl_Brod/publication/232471361_Conceptual...
Brod 2006
Brown 1996
-
- Brown TE. Attention‐Deficit Disorder Scales Manual. San Antonio (TX): Psychological Corporation, 1996.
Brown 2000
-
- Brown TE. Attention Deficit Disorders and Comorbidities in Children, Adolescents and Adults. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Press, 2000.
Campbell 2000
Castells 2013
-
- Castells X, Cunill R, Capellà D. Treatment discontinuation with methylphenidate in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2013;69(3):347‐56. [DOI: 10.1007/s00228-012-1390-7; PUBMED: 22983311] - DOI - PubMed
Chandler 2013
Ciapponi 2011
-
- Ciapponi A, Glujovsky D, Bardach A, García Martí S, Comande D. EROS: A new software for early stage of systematic reviews. HTAi 2011 Conference, 2011 June 27‐29; Rio de Janeiro. 2011.
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioural Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, 1988.
Conners 1999a
-
- Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E. Conners CAARS Adult ADHD Rating Scales: Technical Manual. New York (NY): Multi‐Health Systems Inc., 1999.
Conners 1999b
-
- Conners CK, Erhardt D, Epstein JN, Parker JDA, Sitarenios G, Sparrow E. Self‐ratings of ADHD symptoms in adults I: factor structure and normative data. Journal of Attention Disorders 1999;3(3):141‐51. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479900300303] - DOI
Conners 1999c
-
- Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E. Conners' CAARS Adult ADHD Rating Scales: Technical Manual. Toronto (ON): Multi‐Health Systems, 1999.
Conners 2008
-
- Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow EP. Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale ㅡ Self: Screening Version (CAARS‐S:SV). New South Wales (AU): Psychological Assessments, 2008.
Cunill 2013
Davids 2004
-
- Davids E, Krause DA, Specka M, Gastpar M. Analysis of a special consultation for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults [Analyse einer Spezialsprechstunde für die Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit‐/Hyperaktivitätsstörung bei Erwachsenen]. Gesundheitswesen 2004;66(7):416–22. [DOI: 10.1055/s-2004-813327; PUBMED: 15314733] - DOI - PubMed
Davidson 1960
-
- Davidson HH, Lang G. Children's perceptions of their teachers feelings towards them related to self perception, school achievement and behavior. Journal of Experimental Education 1960;29(2):107‐18. [DOI: 10.1080/00220973.1960.11010675] - DOI
Davidson 2008
Donner 2001
DSM‐5 2013
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5). 5th Edition. Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
DSM‐III‐R 1989
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III‐R). 3rd Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 1989.
DSM‐IV 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
DSM‐IV‐TR 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV‐TR). 4th Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
DuPaul 1990
-
- DuPaul G. The ADHD Rating Scale: normative data, reliability and validity. Unpublished manuscript of the University of Massachussetts Medical School ca 1990.
DuPaul 1998
-
- DuPaul GJ, Power TJ, Anastopoulos AD, Reid R. ADHD Rating Scale‐IV: Checklists, Norms, and Clinical Interpretation. New York (NY): Guilford Press, 1998.
Egger 1997
Endicott 1993
-
- Endicott J, Nee J, Harrison W, Blumenthal R. Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire: a new measure. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1993;29(2):321‐6. [PUBMED: 8290681] - PubMed
Erhardt 1999
-
- Erhardt D, Epstein JN, Conners CK, Parker JDA, Sitarenios G. Self‐ratings of ADHD symptoms in adults: II. Reliability, validity, and diagnostic sensitivity. Journal of Attention Disorders 1999;3(3):153‐8. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479900300304] - DOI
Faraone 2000
-
- Faraone SV, Biederman J, Spencer T, Wilens T, Seidman LJ, Mick E, et al. Attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: an overview. Biological Psychiatry 2000;48(1):9‐20. [PUBMED: 10913503] - PubMed
Gershon 2002
Gittelman 1985
-
- Gittelman R. Self‐evaluation (teenager's) self‐reports. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1985;21:925‐6.
Glujovsky 2010
-
- Glujovsky D, Bardach A, García Martí S, Comande D, Ciapponi A. New software for early stage of systematic reviews. Abstracts of the Joint Cochrane and CampbellColloquium; 2010 Oct 18‐22; Keystone (CO). Chichester (UK): Wiley‐Blackwell, John Wiley & Sons, 2010:P95. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000002; P90] - DOI
Glujovsky 2011
-
- Glujovsky D, Bardach A, García Martí S, Comande D, Ciapponi A. EROS: A new software for early stage of systematic reviews. ISPOR 3rd Latin America Conference: Building Networks Across Institutions for Access to Health Care in Latin America; 2011 Sep 8‐10; Mexico City (MX). Mexico City (MX): IPSOR (International Society for Pharmacoecomics and Outcomes Research), 2011:111.
GRADEpro 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 12 December 2017. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Graham 2011
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W, National Institute of Mental health (US), Psychopharmacology Research Branch. Division of Extramural Research Programs. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology, Revised. Rockville (MD): US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration, National Institute of Mental Health, Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Division of Extramural Research Programs, 1976.
Guyatt 2011
Hamilton 1959
Hamilton 1960
Hesslinger 2002
-
- Hesslinger B, Tebartz Van Elst L, Nyberg E, Dykierek P, Richter H, Berner M, et al. Psychotherapy of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults ‐‐ a pilot study using a structured skills training program. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2002;252(4):177‐84. [DOI: 10.1007/s00406-002-0379-0; PUBMED: 12242579] - DOI - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (Editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jensen 2016
Kaufman 1996
-
- Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Ryan N. Kiddie‐SADS‐Present and Lifetime Version (K‐SADS‐PL). Available from www.psychiatry.pitt.edu/sites/default/files/Documents/assessments/ksads‐... (accessed 12 December 2017).
Kessler 2005
-
- Kessler RC, Adler L, Ames M, Demler O, Faraone S, Hiripi E, et al. The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self‐Report Scale (ASRS): a short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychological Medicine 2005;35(2):245‐56. [PUBMED: 15841682] - PubMed
Kessler 2006
-
- Kessler RC, Akiskal HS, Ames M, Birnbaum H, Greenberg P, Hirschfeld RM, et al. Prevalence and effects of mood disorders on work performance in a nationally representative sample of US workers. American Journal of Psychiatry 2006;163(9):1561‐8. [DOI: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.9.1561; PMC1924724; PUBMED: 16946181] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
King 2006
Knouse 2008
Knouse 2010
Knouse 2017
Landgraf 2007
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Lim 2006
Millstein 1997
-
- Millstein RB, Wilens TE, Biederman J, Spencer TJ. Presenting ADHD symptoms and subtypes in clinically referred adults with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders 1997;2(3):159‐66. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479700200302] - DOI
Moher 2009
Mongia 2012
Morton 2000
Murphy 1996
-
- Murphy K, Barkley RA. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder adults: comorbidities and adaptive impairments. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1996;37(6):393‐401. [PUBMED: 8932963] - PubMed
NIMH 1985
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. CGI (Clinical Global Impression) Scale — NIMH. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1985;21:839‐44.
Perrin 2008
Philipsen 2007
-
- Philipsen A, Richter H, Peters J, Alm B, Sobanski E, Colla M, et al. Structured group psychotherapy in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: results of an open multicenter study. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2007;195(12):1013‐9. [DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0b013e31815c088b; PUBMED: 18091195] - DOI - PubMed
Philipsen 2012
Polanczyk 2014
Prescrire 2007
-
- Prescrire International. Modafinil: serious skin reactions. Prescrire International 2007;16(88):71. [PUBMED: 17465032] - PubMed
Ramsay 2007
-
- Ramsay JR. Current status of cognitive‐behavioral therapy as a psychosocial treatment for adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Current Psychiatry Reports 2007;9(5):427‐33. [PUBMED: 17915084] - PubMed
Ramsay 2008
-
- Ramsay JR, Rostain AL. Cognitive‐Behavioral Therapy for Adult ADHD: An Integrative Psychosocial and Medical Approach. New York (NY): Routledge, 2008.
Ramsay 2010
-
- Ramsay JR. CBT for adult ADHD: adaptations and hypothesized mechanisms of change. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy 2010;24(1):37‐45. [DOI: 10.1891/0889-8391.24.1.37] - DOI
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rosenberg 1965a
-
- Rosenberg M. The association between self‐esteem and anxiety. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1962;1:135‐52. [PUBMED: 13974903] - PubMed
Rosenberg 1965b
-
- Rosenberg M. Society and the Adolescent Self‐Image. Princeton (NJ): Princeton University Press, 1965.
Safren 2006
-
- Safren SA. Cognitive‐behavioral approaches to ADHD treatment in adulthood. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2006;67(Suppl 8):46‐50. [PUBMED: 16961430] - PubMed
Safren 2014 [pers comm]
-
- Safren SA. Random sequence generation and allocation concealment [personal communication]. Email to: S Safren 12 June 2014.
Seidman 2006
Shear 2001
-
- Shear MK, Vander Bilt J, Rucci P, Endicott J, Lydiard B, Otto MW, et al. Reliability and validity of a structured interview guide for the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (SIGH‐A). Depression and Anxiety 2001;13(4):166‐78. [PUBMED: 11413563] - PubMed
Simon 2009
Solanto 2014 [pers comm]
-
- Solanto MV. Random sequence generation and allocation concealment [personal communication]. Email to: M V Solanto 11 June 2014.
Speilberger 1989
-
- Spielberger CD. State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory: A Comprehensive Bibliography. 2nd Edition. Palo Alto (CA): Consulting Psychologists Press, 1989.
Speilberger 1991
-
- Spielberger CD. State‐Trait Anger Expression Inventory: Revised Research Edition: Professional Manual. Odessa (FL): Psychological Assessment Resources, 1991.
Spencer 1998
-
- Spencer T, Biederman J, Wilens TE, Faraone SV. Adults with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a controversial diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59(S7):59‐68. [PUBMED: 9680054] - PubMed
Spielberger 1986
-
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE. STAI: State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory: Manual [STAI: cuestionario de ansiedad estado‐rasgo: Manual]. Madrid (ES): TEA Ediciones, 1986.
Spielberger 1988
-
- Spielberger CD. State‐Trait Anger Expression Inventory: Professional Manual. Odessa (FL): Psychological Assessment resources, 1988.
Still 1902
-
- Still GF. The Goulstonian lectures on some abnormal psychical condition in children. Lancet 1902;159(4104):1163‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)74901-X] - DOI
Torrente 2011
Torrente 2012
-
- Torrente F, López P, Alvarez Prado D, Kichic R, Cetkovich‐Bakmas M, Lischinsky A, et al. Dysfunctional cognitions and their emotional, behavioral, and functional correlates in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): is the cognitive‐behavioral model valid?. Journal of Attention Disorders 2014;18(5):412‐24. [DOI: 10.1177/1087054712443153; PUBMED: 22628149] - DOI - PubMed
Van der Ploeg 2000
-
- Ploeg HM, Defares PB, Spielberger CD. Handleiding bij de Zelf‐Beoordelings Vragenlijst ZBV. Een Nederlandse bewerking van de Speilberger State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory STAI‐DY [Manual for the Self‐Assessment Questionnaire ZBV. A Dutch Version of the Speilberger State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory STAI‐DY]. Amsterdam (NLD): Pearson Assessment and Information BV, 2000.
Virta 2014 [pers comm]
-
- Virta M. Random sequence generation and allocation concealment [personal communication]. Email to: M Virta 17 June 2014.
Weiss 2008
Wender 2001
-
- Wender PH, Wolf LE, Wasserstein J. Adults with ADHD. An overview. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2001;931:1‐16. [PUBMED: 11462736] - PubMed
WHO 1993
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. Diagnostic Criteria for Research. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1993.
Wilens 2002
Wilens 2004
-
- Wilens TE, Dodson W. A clinical perspective of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder into adulthood. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2004;65(10):1301‐11. [PUBMED: 15491232] - PubMed
Wood 1976
Woods 1986
-
- Woods D. The diagnosis and treatment of attention deficit disorder, residual type. Psychiatric Annals 1986;16(1):23‐8. [DOI: 10.3928/0048-5713-19860101-06] - DOI
Young 2007a
-
- Young S, Bramham J. ADHD in Adults: A Psychological Guide to Practice. Chichester (UK): John Wiley and Sons, 2007.
Young 2007b
-
- Young S, Ross RR. R&R2 for ADHD Youths and Adults: A Prosocial Training Program. Ottawa (ON): Cognitive Centre of Canada, 2007.
Young 2014 [pers comm]
-
- Young S. Random sequence generation and allocation concealment [personal communication]. Email to: Susan Young 18 June 2014.
Young 2016
-
- Young Z, Moghaddam N, Tickle A. The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with ADHD: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Attention Disorders 2016 Aug 22 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1177/1087054716664413; PUBMED: 27554190] - DOI - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. [PUBMED: 6880820] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lopez 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

