Renal autoregulation and blood pressure management in circulatory shock
- PMID: 29566705
- PMCID: PMC5865356
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-018-1962-8
Renal autoregulation and blood pressure management in circulatory shock
Abstract
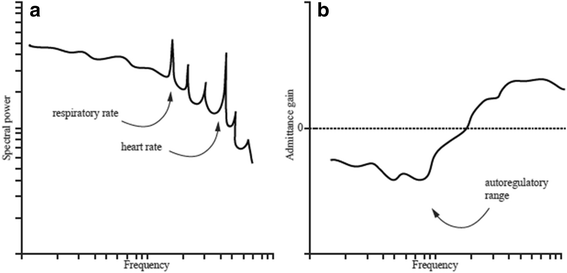
The importance of personalized blood pressure management is well recognized. Because renal pressure-flow relationships may vary among patients, understanding how renal autoregulation may influence blood pressure control is essential. However, much remains uncertain regarding the determinants of renal autoregulation in circulatory shock, including the influence of comorbidities and the effects of vasopressor treatment. We review published studies on renal autoregulation relevant to the management of acutely ill patients with shock. We delineate the main signaling pathways of renal autoregulation, discuss how it can be assessed, and describe the renal autoregulatory alterations associated with chronic disease and with shock.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cardiogenic shock; Hemorrhagic shock; Renal blood flow; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
JLV is Editor-in-Chief of
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
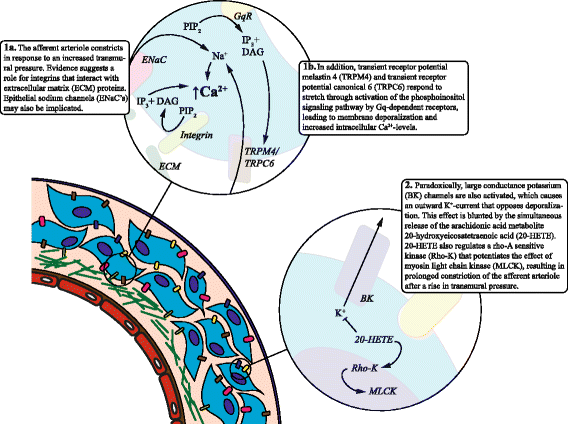
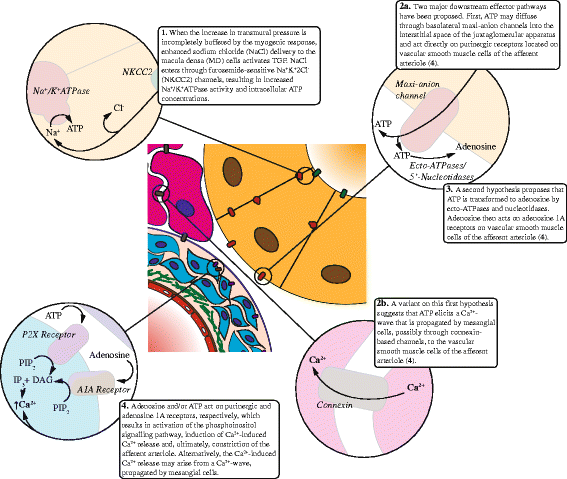
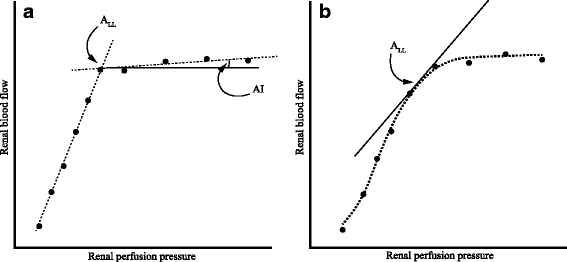
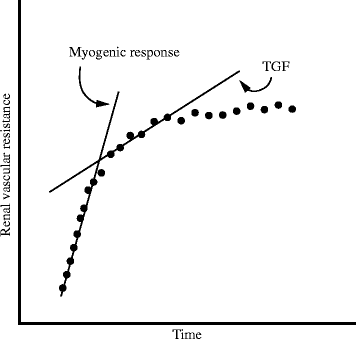
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

