An investigation of the olive phenols activity as a natural medicine
- PMID: 29567235
- PMCID: PMC9322212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.07.003
An investigation of the olive phenols activity as a natural medicine
Abstract
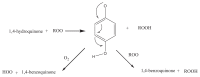
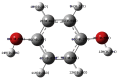
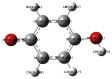
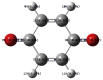
The natural antioxidants of olive oil have phenolic structure and their activities are related to the formation of stable derivatives. In this study, the single components of the phenolic fraction of olive oil (1,4-hydroquinone, Semiquinone and 1,4-benzoquinone) have been studied as theoretical by using DFT (Density functional Theory). The behaviors of phenolic compounds of olive against to the alkyl peroxy radicals were investigated. Our data show that 1,4-benzoquinone is the best electron transfer agent in primary metabolic processes to human life. The frontier orbital gap, namely HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital)-LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) gap is the smallest for 1,4-benzoquinone. Hence, it is more stable than the others in blood. The natural phenolic compound's mechanism of many plants can be explained by using DFT method without consuming time and money. In this study, we have indicated the behaviors of natural antioxidants of olive oil's single components phenolic structure in blood phase.
Keywords: 1,4-Benzoquinone; 1,4-Hydroquinone; Blood; DFT; Semiquinone.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

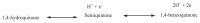
Similar articles
-
New Strategies in the Cultivation of Olive Trees and Repercussions on the Nutritional Value of the Extra Virgin Olive Oil.Molecules. 2020 May 18;25(10):2345. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102345. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32443449 Free PMC article.
-
Applicability of an In-Vitro Digestion Model to Assess the Bioaccessibility of Phenolic Compounds from Olive-Related Products.Molecules. 2021 Nov 3;26(21):6667. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216667. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Phenol-Enriched Olive Oil with Phenolic Compounds Extracted from Wastewater Produced by Physical Refining.Nutrients. 2017 Aug 22;9(8):916. doi: 10.3390/nu9080916. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28829365 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Review on the Significance of Olive Phytochemicals in Plant Physiology and Human Health.Molecules. 2017 Nov 16;22(11):1986. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111986. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29144445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Processing Effect and Characterization of Olive Oils from Spanish Wild Olive Trees (Olea europaea var. sylvestris).Molecules. 2021 Feb 28;26(5):1304. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051304. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33671061 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Drug Design Strategies for the Treatment of Viral Disease. Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Derivatives.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 30;12:709104. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.709104. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34393787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Hansen Solubility Parameters in the Aqueous-Ethanol Extraction of Genistein-7-O-[α-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-glucopyranoside from Derris scandens and Its Molecular Orbital Study on Antioxidant Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 15;26(12):5740. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125740. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Servili M, Selvaggini R, Esposto S, Taticchi A, Montedoro GF, Morozzi GJ. Health and sensory properties of virgin olive oil hydrophilic phenols: agronomic and technological aspect of production that affect their occurrence in the oil. J Chromatogr. 2004;1054:113–27. - PubMed
-
- Servili M, Esposto S, Fabiani R, Urbani S, Taticchi A, Mariucci F, et al. Phenolic compounds in olive oil: antioxidant, health and organoleptic activities according to their chemical structure. Inflammopharmacology. 2009;17:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Bendary E, Francis RR, Ali HMG, Sarwat MI, El Hady S. Antioxidant and structure–activity relationships (SARs) of some phenolic and anilines compounds. Ann Agric Sci. 2013;58(2):173–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
