Effect of drying processes on prenylflavonoid content and antioxidant activity of Epimedium koreanum Nakai
- PMID: 29567251
- PMCID: PMC9322203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.05.011
Effect of drying processes on prenylflavonoid content and antioxidant activity of Epimedium koreanum Nakai
Abstract
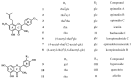
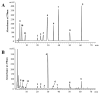
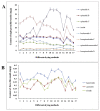
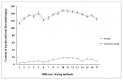
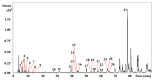
Epimedium koreanum Nakai is a famous Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of impotence, osteoporosis, immune suppression and cardiovascular diseases. Drying is the most common and fundamental procedure in post-harvest processing of E. koreanum, which contributes to the variations of flavonoid content, especially prenylflavonoids, the bioactive components. In present study, effect of drying processes on flavonoid content and antioxidant activity were investigated. High performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detection and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry methods were employed. Twenty seven compounds were identified and 11 of them, including eight prenylflavonoids and three other types of flavonoids, were further quantified. The antioxidant activity of E. koreanum was evaluated by the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl free radical scavenging method. The results showed that content of the eight prenylflavonoids exhibited significant variations after different drying processes, especially icariin and baohuoside I. The variation tendency of antioxidant activity was positively correlated with the content of total flavonoid, afzelin and icariin.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; Drying process; Epimedium koreanum Nakai; Prenylflavonoid; Quantitative analysis.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel online preparative high-performance liquid chromatography system with the multiple trap columns-valve switch technique for the rapid and efficient isolation of main flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum Nakai.J Sep Sci. 2021 Jan;44(2):656-665. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202000783. Epub 2020 Nov 27. J Sep Sci. 2021. PMID: 33151025
-
Identification and characterization of active compounds and their metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography/Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry after oral administration of a herbal extract of Epimedium koreanum Nakai to rats.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008 Sep;22(18):2813-24. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3664. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008. PMID: 18712702
-
A new flavonol glycoside from the aerial parts of Epimedium koreanum Nakai.Nat Prod Res. 2017 Feb;31(3):320-325. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2016.1239092. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Nat Prod Res. 2017. PMID: 27690633
-
Advancements in the Biotransformation and Biosynthesis of the Primary Active Flavonoids Derived from Epimedium.Molecules. 2023 Oct 19;28(20):7173. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207173. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Preparation method and pharmacological effect of baohuoside Ⅰ].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Sep;43(17):3444-3450. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180702.007. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30347910 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of Epicedium treatment for depression based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Sep 3;21(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03389-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34479552 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro evaluation of the anti-pancreatic cancer activity of epimedium herb.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 1;15:1389221. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389221. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39011503 Free PMC article.
-
Epimedium koreanum Extract and Its Flavonoids Reduced Atherosclerotic Risk via Suppressing Modification of Human HDL.Nutrients. 2019 May 18;11(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/nu11051110. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31109081 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative and qualitative analyses of cytotoxic triterpenoids in the rhizomes of Anemone raddeana using HPLC and HPLC-ESI-Q/TOF-MS.J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Jul;26(3):1113-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.01.011. Epub 2018 Feb 15. J Food Drug Anal. 2018. PMID: 29976404 Free PMC article.
-
A potential therapeutic effect of sea cucumber Holothuria polii extract during the intestinal phase of experimental trichinellosis.J Parasit Dis. 2025 Mar;49(1):224-241. doi: 10.1007/s12639-024-01737-4. Epub 2024 Oct 14. J Parasit Dis. 2025. PMID: 39975624
References
-
- National Commission of Chinese. Pharmacopoeia Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2015.
-
- Hang DX, Yang J, Lu XM, Deng Y, Xiong ZL, Li FM. An integrated plasma and urinary metabonomic study using UHPLC–MS: intervention effects of Epimedium koreanum on ‘Kidney-Yang Deficiency syndrome’ rats. J Pharm Biomed. 2013;76:200–6. - PubMed
-
- Xu FF, Ding Y, Guo YY, Liu BY, Kou ZN, Xiao W, et al. Anti-osteoporosis effect of Epimedium via an estrogen-like mechanism based on a system-level approach. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;177:148–60. - PubMed
-
- Fan YP, Ren MM, Hou WF, Guo C, Tong DW, Ma L, et al. The activation of Epimedium polysaccharide-propolis flavones liposome on Kupffer cells. Carbohyd Polym. 2015;133:613–23. - PubMed
-
- Inokuchi J, Okabe H, Yamauch T, Nagamatsu A. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme in crude drugs. I. Chem Pharm Bull. 1984;32:3615–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
