Radionuclide Imaging-Guided Chemo-Radioisotope Synergistic Therapy Using a 131I-Labeled Polydopamine Multifunctional Nanocarrier
- PMID: 29567310
- PMCID: PMC5993982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.019
Radionuclide Imaging-Guided Chemo-Radioisotope Synergistic Therapy Using a 131I-Labeled Polydopamine Multifunctional Nanocarrier
Abstract
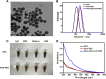
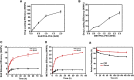
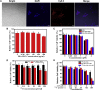
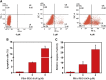
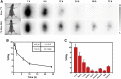
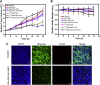
Development of biocompatible nanomaterials with multiple functionalities for combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy has attracted tremendous attention in cancer treatment. Herein, poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) modified polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles were successfully developed as a favorable biocompatible nanoplatform for co-loading antitumor drugs and radionuclides to achieve imaging-guided combined radio-chemotherapy. It is demonstrated that PEGylated PDA nanoparticles can effectively load two different drugs including sanguinarine (SAN) and metformin (MET), as well as radionuclides 131I in one system. The loaded SAN and MET could inhibit tumor growth via inducing cell apoptosis and relieving tumor hypoxia, while labeling PDA-PEG with 131I enables in vivo radionuclide imaging and radioisotope therapy. As revealed by the therapeutic efficacy both in cell and animal levels, the multifunctional PDA nanoparticles (131I-PDA-PEG-SAN-MET) can effectively repress the growth of cancer cells in a synergistic manner without significant toxic side effects, exhibiting superior treatment outcome than the respective monotherapy. Therefore, this study provides a promising polymer-based platform to realize imaging-guided radioisotope/chemotherapy combination cancer treatment in future clinical application.
Keywords: PDA nanoparticles; metformin; radionuclide imaging; sanguinarine; synergistic therapy.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polydopamine Coated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as a Versatile Platform with Radionuclide Labeling for Multimodal Tumor Imaging and Therapy.Theranostics. 2016 Jul 18;6(11):1833-43. doi: 10.7150/thno.16047. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 27570554 Free PMC article.
-
Polydopamine Nanoparticles as a Versatile Molecular Loading Platform to Enable Imaging-guided Cancer Combination Therapy.Theranostics. 2016 Apr 28;6(7):1031-42. doi: 10.7150/thno.14431. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 27217836 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted polydopamine nanoparticles enable photoacoustic imaging guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of tumor.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 1;47:124-134. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27721008
-
Application of polydopamine in tumor targeted drug delivery system and its drug release behavior.J Control Release. 2018 Nov 28;290:56-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30312718 Review.
-
Polydopamine Nanomaterials for Overcoming Current Challenges in Cancer Treatment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 May 17;13(10):1656. doi: 10.3390/nano13101656. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methods for Radiolabelling Nanoparticles: SPECT Use (Part 1).Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 20;12(10):1522. doi: 10.3390/biom12101522. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanin nanoparticles alleviate sepsis-induced myocardial injury by suppressing ferroptosis and inflammation.Bioact Mater. 2022 Dec 27;24:313-321. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.12.026. eCollection 2023 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 36632502 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Therapeutic Effects of 131I-Labeled and 5Fu-Loaded Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Apr 23;15:2777-2787. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S215137. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32368054 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia With Radionuclide-Labeled Tracers for PET.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 7;11:731503. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.731503. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34557414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanin and Melanin-Functionalized Nanoparticles as Promising Tools in Cancer Research-A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;14(7):1838. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071838. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Corsini M.M., Miller R.C., Haddock M.G., Donohue J.H., Farnell M.B., Nagorney D.M., Jatoi A., McWilliams R.R., Kim G.P., Bhatia S. Adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy for pancreatic carcinoma: the Mayo Clinic experience (1975-2005) J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3511–3516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

