Effect of scaling and root planing on gingival crevicular fluid level of YKL-40 acute phase protein in chronic periodontitis patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clinico-biochemical study
- PMID: 29568171
- PMCID: PMC5855268
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_95_17
Effect of scaling and root planing on gingival crevicular fluid level of YKL-40 acute phase protein in chronic periodontitis patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clinico-biochemical study
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) levels of YKL-40 acute phase protein in chronic periodontitis (CP) with and without type 2 diabetes and also to assess the effect of periodontal therapy (scaling and root planing [SRP]) on this GCF biomarker and the clinical parameters. YKL-40 is derived from tyrosine (Y), lysine (K), and leucine (L) with a molecular weight of 40 kDa.
Materials and methods: A total of 105 individuals (30-60 years) were grouped as 35 individuals each in three groups (Group I - healthy; Group II - CP with diabetes mellitus [DM]; and Group III - CP). Clinical parameters including plaque index, gingival index, probing pocket depth, and clinical attachment level followed by GCF sample collection from test sites were done at baseline and 6 weeks after SRP (among Group II and Group III patients). GCF YKL-40 level was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
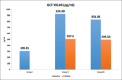
Results: The mean GCF YKL-40 level at baseline was significantly lower for Group I (309.81 ± 124.93 pg/ml) as compared to Group II (924.88 ± 415.28 pg/ml) and Group III (834.08 ± 270.42 pg/ml), respectively (P < 0.001). The level reduced significantly 6 weeks after SRP for Group II (507.6 ± 265.03 pg/ml) and Group III (499.54 ± 293.38 pg/ml) (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The level of GCF YKL-40 in CP patients with or without DM is higher than healthy individuals and the level reduced 6 weeks post-SRP among Group II and Group III. Hence, YKL-40 can be considered as an important biomarker in the diagnosis of CP.
Keywords: Biomarkers; chronic periodontitis; diabetes mellitus; gingival crevicular fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
YKL-40 level in gingival crevicular fluid from patients with periodontitis and type 2 diabetes.Oral Dis. 2015 Jul;21(5):667-73. doi: 10.1111/odi.12334. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 25740558
-
Effects of scaling and root planing on gingival crevicular fluid vascular endothelial growth factor level in chronic periodontitis patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A clinicobiochemical study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2016 May-Jun;20(3):244-8. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.176395. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2016. PMID: 27563195 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of scaling and root planing on C-reactive protein levels in gingival crevicular fluid and serum in chronic periodontitis patients with or without diabetes mellitus.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2014 Aug;44(4):158-68. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2014.44.4.158. Epub 2014 Aug 28. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25177517 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of scaling and root planing and subantimicrobial dose doxycycline on gingival crevicular fluid levels of matrix metalloproteinase-8, -13 and serum levels of HsCRP in patients with chronic periodontitis.J Periodontol. 2010 Aug;81(8):1132-9. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090694. J Periodontol. 2010. PMID: 20370419 Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus on resistin levels of gingival crevicular fluid- a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025 May-Jun;15(3):612-623. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.03.022. Epub 2025 Apr 8. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025. PMID: 40248519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of blood glucose, helper T cells and cytokine levels with degree of periodontal lesion in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients accompanied by chronic periodontitis.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Jun;23(2):239-245. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i2.27. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38223593 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and immune responses to neoadjuvant fulvestrant with or without enzalutamide in ER+/Her2- breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2024 Oct 6;10(1):88. doi: 10.1038/s41523-024-00697-5. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39368973 Free PMC article.
-
Nonsurgical Periodontal Therapy Reduces Salivary and Gingival Crevicular Fluid YKL-40 and IL-6 Levels in Chronic Periodontitis.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020 Sep 4;18(4):815-822. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a45086. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020. PMID: 32895666 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous and microbial biomarkers for periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 5;14:1292596. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1292596. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38149100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grossi SG, Genco RJ, Machtei EE, Ho AW, Koch G, Dunford R, et al. Assessment of risk for periodontal disease. II. Risk indicators for alveolar bone loss. J Periodontol. 1995;66:23–9. - PubMed
-
- Kido J, Bando Y, Bando M, Kajiura Y, Hiroshima Y, Inagaki Y, et al. YKL-40 level in gingival crevicular fluid from patients with periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. Oral Dis. 2015;21:667–73. - PubMed
-
- Jin Y, Cao JN, Wang CX, Feng QT, Ye XH, Xu X, et al. High serum YKL-40 level positively correlates with coronary artery disease. Biomark Med. 2017;11:133–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous