Many Routes to an Antibody Heavy-Chain CDR3: Necessary, Yet Insufficient, for Specific Binding
- PMID: 29568296
- PMCID: PMC5852061
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00395
Many Routes to an Antibody Heavy-Chain CDR3: Necessary, Yet Insufficient, for Specific Binding
Abstract
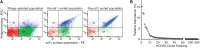
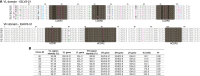
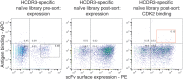
Because of its great potential for diversity, the immunoglobulin heavy-chain complementarity-determining region 3 (HCDR3) is taken as an antibody molecule's most important component in conferring binding activity and specificity. For this reason, HCDR3s have been used as unique identifiers to investigate adaptive immune responses in vivo and to characterize in vitro selection outputs where display systems were employed. Here, we show that many different HCDR3s can be identified within a target-specific antibody population after in vitro selection. For each identified HCDR3, a number of different antibodies bearing differences elsewhere can be found. In such selected populations, all antibodies with the same HCDR3 recognize the target, albeit at different affinities. In contrast, within unselected populations, the majority of antibodies with the same HCDR3 sequence do not bind the target. In one HCDR3 examined in depth, all target-specific antibodies were derived from the same VDJ rearrangement, while non-binding antibodies with the same HCDR3 were derived from many different V and D gene rearrangements. Careful examination of previously published in vivo datasets reveals that HCDR3s shared between, and within, different individuals can also originate from rearrangements of different V and D genes, with up to 26 different rearrangements yielding the same identical HCDR3 sequence. On the basis of these observations, we conclude that the same HCDR3 can be generated by many different rearrangements, but that specific target binding is an outcome of unique rearrangements and VL pairing: the HCDR3 is necessary, albeit insufficient, for specific antibody binding.
Keywords: binding specificity; heavy-chain complementarity-determining region 3; inverse PCR; rearrangement; single-chain Fv display.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Ig heavy chain CDR3 regions in adult bone marrow pre-B cells display an adult phenotype of diversity: evidence for structural selection of DH amino acid sequences.Int Immunol. 1997 Oct;9(10):1503-15. doi: 10.1093/intimm/9.10.1503. Int Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9352355
-
Antibody VH and VL recombination using phage and ribosome display technologies reveals distinct structural routes to affinity improvements with VH-VL interface residues providing important structural diversity.MAbs. 2014 Jan-Feb;6(1):236-45. doi: 10.4161/mabs.27261. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24256948 Free PMC article.
-
Non-immunized natural human heavy chain CDR3 repertoires allow the isolation of high affinity peptides mimicking a human influenza hemagglutinin epitope.Mol Immunol. 2008 Mar;45(5):1366-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17936360
-
Primer Design and Inverse PCR on Yeast Display Antibody Selection Outputs.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1721:35-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7546-4_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423845 Review.
-
Regulation of the antibody repertoire through control of HCDR3 diversity.Vaccine. 1998 Aug-Sep;16(14-15):1383-90. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(98)00096-6. Vaccine. 1998. PMID: 9711776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Direct selection of functional fluorescent-protein antibody fusions by yeast display.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 24;18(2):e0280930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280930. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36827414 Free PMC article.
-
Seeking high-priority mutations enabling successful antibody-breeding: systematic analysis of a mutant that gained over 100-fold enhanced affinity.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 16;10(1):4807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61529-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32179767 Free PMC article.
-
Rationalizing Random Walks: Replicating Protective Antibody Trajectories.Trends Immunol. 2021 Mar;42(3):186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33514459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress and challenges for the machine learning-based design of fit-for-purpose monoclonal antibodies.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2008790. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.2008790. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 35293269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a Large Size Human Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Variable (VH) Domain Library, Isolation and Characterization of Novel Human Antibody VH Domains Targeting PD-L1 and CD22.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:869825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869825. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zemlin M, Klinger M, Link J, Zemlin C, Bauer K, Engler JA, et al. Expressed murine and human CDR-H3 intervals of equal length exhibit distinct repertoires that differ in their amino acid composition and predicted range of structures. J Mol Biol (2003) 334(4):733–49. 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matsuda F, Shin EK, Hirabayashi Y, Nagaoka H, Yoshida MC, Zong SQ, et al. Organization of variable region segments of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain: duplication of the D5 cluster within the locus and interchromosomal translocation of variable region segments. EMBO J (1990) 9(8):2501–6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

