Methotrexate sensitizes drug-resistant metastatic melanoma cells to BRAF V600E inhibitors dabrafenib and encorafenib
- PMID: 29568360
- PMCID: PMC5862581
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24341
Methotrexate sensitizes drug-resistant metastatic melanoma cells to BRAF V600E inhibitors dabrafenib and encorafenib
Abstract
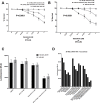
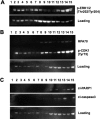
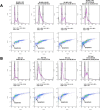
Acquired resistance of metastatic melanoma (MM) tumors to BRAF V600E inhibitors (BRAFi's) is commonplace in the clinic. Habitual relapse of patients contributes to <20% 5-year survival rates in MM. We previously identified serine synthesis as a critical detrminant of late-stage cancer cell resistance to BRAFi's. Pre-treatment with DNA damaging agent gemcitabine (a nucleoside analog) re-sensitized drug-resistant cancer cells to BRAFi's dabrafenib and vemurafenib. Importantly, the combination treatments were effective against BRAF wild type cancer cells potentially expanding the clinical reach of BRAFi's. In this study, we identify the antifolate methotrexate (MTX) as a sensitizer of acquired- and intrinsically-resistant MM cells to BRAFi's dabrafenib and encorafenib. We identify a novel, positive correlation between dabrafenib treatments and repair delay of MTX induced single-strand DNA (ssDNA) breaks. Cells arrest in G1 phase following simultaneous MTX + dabrafenib treatments and eventually die via apoptosis. Importantly, we identify RAS codon 12 activating mutations as prognostic markers for MTX + BRAFi treatment efficacy. We describe a method of killing drug-resistant MM cells that if translated has the potential to improve MM patient survival.
Keywords: dabrafenib; encorafenib; metastatic melanoma; methotrexate; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST T.J. Yen is a consultant/advisory board member for Evol Science. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway overcomes the stimulating effect of dabrafenib on the invasive behavior of melanoma cells with acquired resistance to the BRAF inhibitor.Int J Oncol. 2016 Sep;49(3):1164-74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3594. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27572607
-
Dabrafenib in the treatment of advanced melanoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2013 Jun;49(6):377-85. doi: 10.1358/dot.2013.49.6.1968669. Drugs Today (Barc). 2013. PMID: 23807941 Review.
-
Fertility Outcomes and Sperm-DNA Parameters in Metastatic Melanoma Survivors Receiving Vemurafenib or Dabrafenib Therapy: Case Report.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 5;10:232. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00232. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32211316 Free PMC article.
-
Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib.N Engl J Med. 2015 Jan 1;372(1):30-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412690. Epub 2014 Nov 16. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25399551 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical development of dabrafenib in BRAF mutant melanoma and other malignancies.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013 Jul;9(7):893-9. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2013.794220. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23621583 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Research Progress of Chiral Small Molecular Antitumor-Targeted Drugs Approved by the FDA From 2011 to 2019.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 17;11:785855. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.785855. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34976824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Effect of the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib in 2D and 3D Cell Culture Models of Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells.In Vivo. 2024 Jul-Aug;38(4):1579-1593. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13608. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38936891 Free PMC article.
-
Encorafenib Acts as a Dual-Activity Chemosensitizer through Its Inhibitory Effect on ABCC1 Transporter In Vitro and Ex Vivo.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 24;14(12):2595. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122595. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559089 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-3662 targets ZEB1 and attenuates the invasion of the highly aggressive melanoma cell line A375.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jun 28;11:5845-5856. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S200540. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31388313 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of high-dimensional omics-derived predictors for tumor growth dynamics using machine learning and pharmacometric modeling.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;10(4):350-361. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12603. Epub 2021 Apr 8. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33792207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross KC, Andrews AJ, Marion CD, Yen TJ, Bhattacharjee V. Identification of the serine biosynthesis pathway as a critical component of BRAF inhibitor resistance of melanoma, pancreatic, and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:1596–1609. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0798. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fedorenko IV, Paraiso KH, Smalley KS. Acquired and intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E mutant melanoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82:201–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W, Davis N, Dicks E, Ewing R, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00766. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, Kumar M, Rishi I, Gerrero R, Einhorn E, Herlyn M, Minna J, Nicholson A, Roth JA, Albelda SM, Davies H, et al. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6997–7000. - PubMed
-
- Spagnolo F, Ghiorzo P, Queirolo P. Overcoming resistance to BRAF inhibition in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5:10206–21. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2602. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

