Ex situ generation of stoichiometric HCN and its application in the Pd-catalysed cyanation of aryl bromides: evidence for a transmetallation step between two oxidative addition Pd-complexes
- PMID: 29568458
- PMCID: PMC5855124
- DOI: 10.1039/c7sc03912c
Ex situ generation of stoichiometric HCN and its application in the Pd-catalysed cyanation of aryl bromides: evidence for a transmetallation step between two oxidative addition Pd-complexes
Abstract
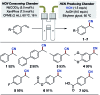
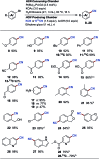
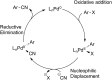
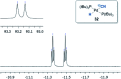
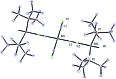
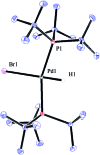
A protocol for the Pd-catalysed cyanation of aryl bromides using near stoichiometric and gaseous hydrogen cyanide is reported for the first time. A two-chamber reactor was adopted for the safe liberation of ex situ generated HCN in a closed environment, which proved highly efficient in the Ni-catalysed hydrocyanation as the test reaction. Subsequently, this setup was exploited for converting a range of aryl and heteroaryl bromides (28 examples) directly into the corresponding benzonitriles in high yields, without the need for cyanide salts. Cyanation was achieved employing the Pd(0) precatalyst, P(tBu)3-Pd-G3 and a weak base, potassium acetate, in a dioxane-water solvent mixture. The methodology was also suitable for the synthesis of 13C-labelled benzonitriles with ex situ generated 13C-hydrogen cyanide. Stoichiometric studies with the metal complexes were undertaken to delineate the mechanism for this catalytic transformation. Treatment of Pd(P(tBu)3)2 with H13CN in THF provided two Pd-hydride complexes, (P(tBu)3)2Pd(H)(13CN), and [(P(tBu)3)Pd(H)]2Pd(13CN)4, both of which were isolated and characterised by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystal structure analysis. When the same reaction was performed in a THF : water mixture in the presence of KOAc, only (P(tBu)3)2Pd(H)(13CN) was formed. Subjection of this cyano hydride metal complex with the oxidative addition complex (P(tBu)3)Pd(Ph)(Br) in a 1 : 1 ratio in THF led to a transmetallation step with the formation of (P(tBu)3)2Pd(H)(Br) and 13C-benzonitrile from a reductive elimination step. These experiments suggest the possibility of a catalytic cycle involving initially the formation of two Pd(ii)-species from the oxidative addition of L n Pd(0) into HCN and an aryl bromide followed by a transmetallation step to L n Pd(Ar)(CN) and L n Pd(H)(Br), which both reductively eliminate, the latter in the presence of KOAc, to generate the benzonitrile and L n Pd(0).
Figures




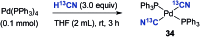
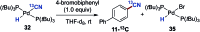







References
-
- Pollak P., Romeder G., Hagedorn F. and Gelbke H. P., Nitriles, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, June 15, 2000, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14356007.a17_363/full.
- Miller J. S., Manson J. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001;34:563. - PubMed
- Kleemann A., Engel J., Kutscher B. and Reichert D., Pharmaceutical substances: Syntheses, Patents, Applications of the most relevant APIs, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York, 2001.
- Goujon L. J., Khaldi A., Maziz A., Plesse C., Nguyen G. T. M., Aubert P.-H., Vidal F., Chevrot C., Teyssié D. Macromolecules. 2011;44:9683.
- Fleming F. F. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1999;16:597.
- Torborg C., Beller M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009;351:3027.
-
- Rappoport Z., The Chemistry of the Cyano Group, Interscience Publisher, New York, 1970.
-
- Rosenmund K. W., Struck E. Chem. Ber. 1919;52:1749.
- Lindley J. Tetrahedron. 1984;40:1433.
- Sandmeyer T. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1884;17:1633.
- Hodgson H. H. Chem. Rev. 1947;40:251. - PubMed
- Kochi J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957;79:2942.
-
-
For a recent review see:
- Wen Q., Jin J., Zhang L., Luo Y., Lu P., Wang P. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014;55:1271.
- Zanon J., Klapars A., Buchwald S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:2890. - PubMed
- Cristau H.-J., Ouali A., Spindler J.-F., Taillefer M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2005;11:2483. - PubMed
- Schareina T., Zapf A., Mägerlein W., Müller N., Beller M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2007;13:6249. - PubMed
- Schareina T., Zapf A., Cotté A., Gotta M., Beller M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011;353:777.
-
-
- Cassar L. J. Organomet. Chem. 1973;54:C57.
- Cassar L., Ferrara S., Foa M. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1974;132:252.
- Cassar L., Foa M., Montanari F., Marinelli G. P. J. Organomet. Chem. 1979;173:335.
- Sakakibara Y., Okuda F., Shimobayashi A., Kirino K., Sakai M., Uchino N., Takagi K. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1988;61:1985.
- Takagi K., Sakakibara Y. Chem. Lett. 1989;18:1957.
- Sasaki K., Sakai M., Sakakibara Y., Takagi K. Chem. Lett. 1991;20:2017.
- Sakakibara Y., Ido Y., Sasaki K., Saki M., Uchino N. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1993;66:2776.
- Sakakibara Y., Sasaki K., Okuda F., Hokimoto A., Ueda T., Sakai M., Takagi K. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2004;77:1013.
- Arvela R. K., Leadbeater N. E. J. Org. Chem. 2003;68:9122. - PubMed
- Zhang X., Xia A., Chen H., Liu Y. Org. Lett. 2017;19:2118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

