Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells attenuated paraquat-induced acute lung injury via miR-141-3p-Notch-Nrf2 axis
- PMID: 29568483
- PMCID: PMC5859660
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-018-0219-1
Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells attenuated paraquat-induced acute lung injury via miR-141-3p-Notch-Nrf2 axis
Abstract
Background: Paraquat (PQ) presents with high toxicity for humans and animals, and the lungs become the main target organ by the poisoning of PQ leading to acute lung injury. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) were proved to have the repair function on acute lung injury (ALI). We aimed to invatigate the underlying mechanism of EPCs in PQ-induced ALI involving miR-141-3p.
Methods: Endothelial progenitor cells were isolated from peripheral blood of C57BL/6J mice and identified by flow cytometry. Lung wet-to-dry (W/D) weight ratios, lung injury score and the number of total leukocyte and the number of neutrophils in BALF were used to analyze the degree of lung injury. The transfection was performed with Lipofectamine 2000. The levels of miRNA and mRNA were determined by qRT-PCR, and the protein levels were detected by Western blot assay.
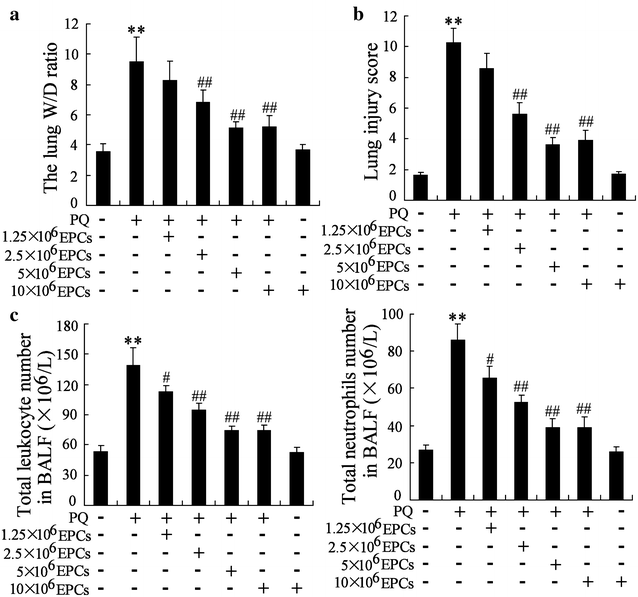
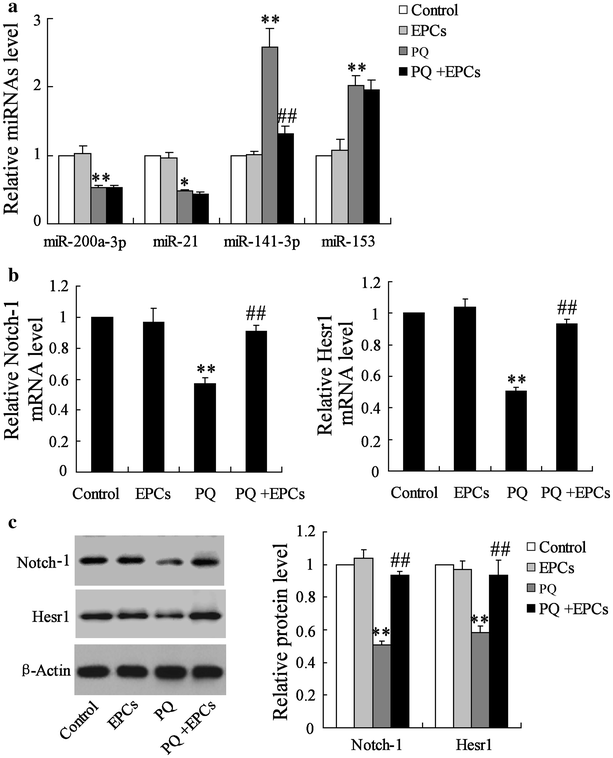
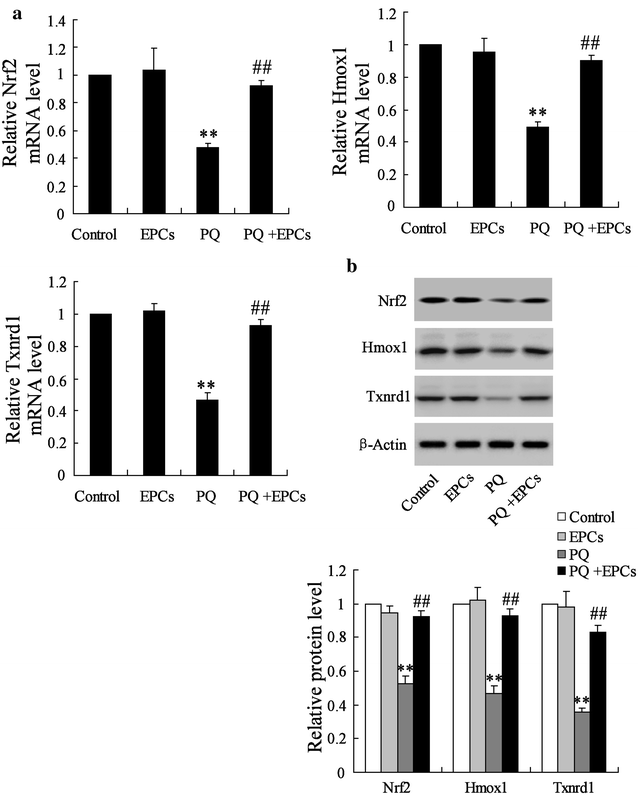
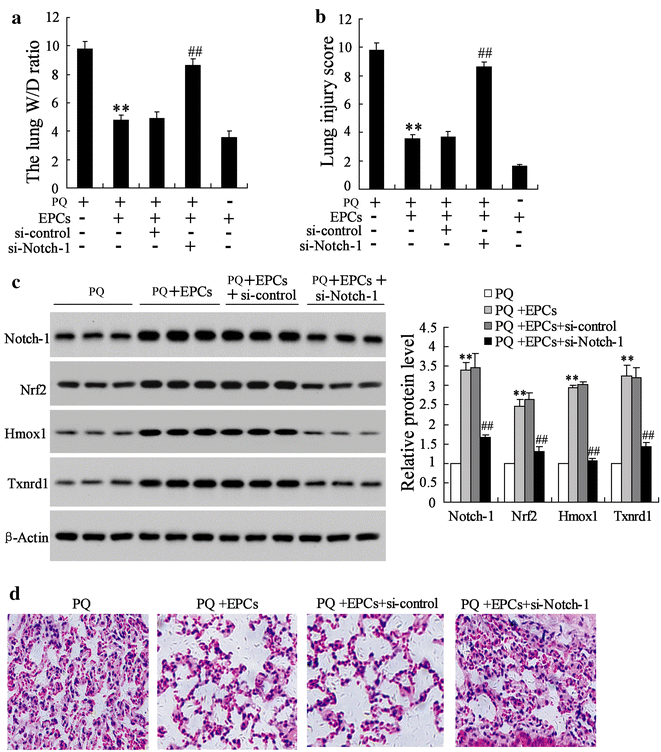
Results: Endothelial progenitor cells alleviated lung wet-to-dry (W/D) weight ratios, lung injury score and the number of total leukocyte and the number of neutrophils in BALF in PQ-induced ALI mice. EPCs inhibited miR-141-3p expression, and enhanced the levels of Notch-Nrf2 axis in PQ-induced ALI mice. MiR-141-3p knockdown reversed the PQ induced-inhibition on Notch-1 and Hesr1 expression. MiR-141-3p over-expression could inhibit the expression of Notch-1 pathway significantly in the pulmonary epithelial cell line MLE-12. Both miR-141-3p over-expression and si-Notch-1 abolished the protection effect of EPCs on lung injury induced by PQ in vivo.
Conclusions: Endothelial progenitor cells could provide therapeutic effect on PQ-induced ALI via miR-141-3p-Notch-Nrf2 Axis.
Keywords: ALI; EPC; Notch-Nrf2 axis; PQ; miR-141-3p.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Andrographolide alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(6):653-661. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68827.15000. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37275765 Free PMC article.
-
circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Feb 28;17(1):403-413. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0417. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. Retraction in: Open Med (Wars). 2023 Dec 31;18(1):20230891. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0891. PMID: 35291714 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dexmedetomidine protects against acute lung injury in mice via the DUSP1/MAPK/NF-κB axis by inhibiting miR-152-3p.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2022 May 9:102131. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2022.102131. Online ahead of print. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35551994
-
Nrf2-regulated miR-380-3p Blocks the Translation of Sp3 Protein and Its Mediation of Paraquat-Induced Toxicity in Mouse Neuroblastoma N2a Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Oct 1;171(2):515-529. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz162. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31368498 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17A Plays the Same Role on Mice Acute Lung Injury Respectively Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and Paraquat.Inflammation. 2017 Oct;40(5):1509-1519. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0592-7. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28600744
Cited by
-
miR-141-3p attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress-induced pulmonary fibrosis in ARDS via the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.Immunol Res. 2024 Oct;72(5):1003-1017. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09503-7. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38865000
-
Exosome-derived circTRPS1 promotes malignant phenotype and CD8+ T cell exhaustion in bladder cancer microenvironments.Mol Ther. 2022 Mar 2;30(3):1054-1070. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.022. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35038580 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrahydroquinone-2-6-disulfonate is a novel, powerful antidote for paraquat poisoning.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 11;11(1):20159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99591-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34635711 Free PMC article.
-
E2F1 regulates miR-215-5p to aggravate paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis via repressing BMPR2 expression.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022 Oct 25;11(6):940-950. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfac071. eCollection 2022 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36569483 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nrf2 and Its Activators in Cardiocerebral Vascular Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Aug 5;2020:4683943. doi: 10.1155/2020/4683943. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32831999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Du Y, Mou Y. Predictive value of 3 methods in severity evaluation and prognosis of acute paraquat poisoning. J Cent S Univ. 2013;38(7):737–742. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

