Combined prediction of miR-210 and miR-374a for severity and prognosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 29568675
- PMCID: PMC5853646
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.835
Combined prediction of miR-210 and miR-374a for severity and prognosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background and aim: Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a disorder featured by hypoxic and ischemic damages during the perinatal period and its high mortality (i.e., 15%-20%) could be partly attributed to late diagnosis. Therefore, miR-210 and miR-374a were investigated to find if they could improve the diagnostic values of S100B protein and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) for HIE.
Methods: Altogether 167 HIE newborns and 82 healthy newborns were recruited, and their blood were sampled for determining the levels of biomarkers. Specifically, S100B protein and NSE levels were detected based on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit, while the expressions of miR-210 and miR-374a were quantified by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Moreover, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were established to assess the diagnostic values of the above biomarkers for HIE. Finally, the correlation analysis between miR-210/miR-374 and Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessment (NBNA) scoring or Gesell intellectual development were also conducted.
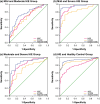
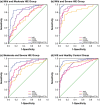
Results: The levels of miR-210, miR-374a, S100B protein, and NSE were significantly distinct between HIE patients and healthy newborns (p < .05). Besides, miR-210 (rs = .573), miR-374a (rs = .651), NSE level (rs = -.622), and S100B level (rs = -.55) were all, respectively, correlated with NBNA scoring with statistical significance (p < .05). Furthermore, it was revealed that the combined diagnosis of miR-210, miR-374a, S100B protein, and NSE could obtain the highest accuracy regarding pairs of mild HIE versus moderate HIE (AUC = 0.898), moderate HIE versus severe HIE (AUC = 0.922), mild HIE versus severe HIE (AUC = 0.996), and HIE versus control (AUC = 0.960). More than that, the four molecules were also remarkably associated with Gesell intellectual development (p < .05).
Conclusion: MiR-210 and miR-374a could help to elevate the diagnostic value and prognostic prediction of S100B protein and NSE for HIE.
Keywords: combined diagnosis; hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy; miR‐210; miR‐374a; prognosis; receiver operating characteristic curve.
Figures


References
-
- Azuma, J. , Nabatame, S. , Nakano, S. , Iwatani, Y. , Kitai, Y. , Tominaga, K. , … Ozono, K. (2015). Prognostic factors for acute encephalopathy with bright tree appearance. Brain & Development, 37(2), 191–199. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. (2004). Exploration the diagnostic criteria for neonatal hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy. Journal of Clinical Pediatrics, 22(11), 712–713.
-
- Chen, X. W. , & Yu, R. J. (2004). Diagnose and treatment for neonatal hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 42(12), 940–941. - PubMed
-
- Cowan, F. , Rutherford, M. , Groenendaal, F. , Eken, P. , Mercuri, E. , Bydder, G. M. , … de Vries, L. S. (2003). Origin and timing of brain lesions in term infants with neonatal encephalopathy. Lancet, 361(9359), 736–742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

