Effects of consumption of whole grape powder on basal NF-κB signaling and inflammatory cytokine secretion in a mouse model of inflammation
- PMID: 29568797
- PMCID: PMC5858739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnim.2017.11.002
Effects of consumption of whole grape powder on basal NF-κB signaling and inflammatory cytokine secretion in a mouse model of inflammation
Abstract
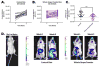
Dietary consumption of polyphenol-rich fruits, such as grapes, may reduce inflammation and potentially prevent diseases linked to inflammation. Here, we used a genetically engineered murine model to measure Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) activity and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion to test the hypothesis that oral consumption of whole grape formulation reduces inflammatory signaling in the body. NF-κB luciferase reporter mice were divided into two groups, one which was fed an experimental diet formulated with 4% (w/w) whole grape powder (WGP) or another which was fed a control diet formulated with 3.6% glucose/fructose (w/w) combination. Simulated inflammation was induced in the mice by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In vivo imaging was used to determine the effect of each diet on NF-κB activity. We found that there were no significant differences in weight gain between the WGP and control diet groups. However, there was a statistically significant (p<0.0001) difference in the progression of basal levels of NF-κB signaling between mice fed on control or WGP diet. There were no significant differences in NF-κB reporter indices between WGP- and control-diet groups after either acute or repeated inflammatory challenge. However, terminal blood collection revealed significantly (p<0.01) lower serum concentrations of the inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNFα) only among WGP diet mice subjected to acute inflammatory challenge. Overall, these data suggest that while diets supplemented with WGP may suppress steady-state low levels of inflammatory signaling, such a supplementation may not alleviate exogenously induced massive NF-κB activation.
Keywords: NF-kB; Whole grape powder; diet; in vivo; inflammation; mouse.
Figures
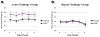



Similar articles
-
Medium-chain triglyceride ameliorates insulin resistance and inflammation in high fat diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Apr;55(3):931-40. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0907-0. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25911003
-
Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor activation in the alleviation of intestinal inflammation in a piglet model by dietary aromatic amino acid supplementation.Br J Nutr. 2018 Dec;120(12):1321-1331. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518002891. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30375295
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidins from wild grape (Vitis amurensis) seeds in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:409321. doi: 10.1155/2013/409321. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 24260615 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of NF-κB sensing and interleukin-4 secreting mesenchymal stromal cells as an "on-demand" drug delivery system to modulate inflammation.Cytotherapy. 2017 Sep;19(9):1025-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Cytotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28739167 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and anti hyperglycemic role of wine grape powder in rats fed with a high fructose diet.Biol Res. 2015 Sep 30;48:53. doi: 10.1186/s40659-015-0045-4. Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 26420015 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long Non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), A New Target in Stroke.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;42(3):501-519. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00954-8. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 32865676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRD4 promotes tumor progression and NF-κB/CCL2-dependent tumor-associated macrophage recruitment in GIST.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Dec 9;10(12):935. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2170-4. Cell Death Dis. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Death Dis. 2025 Mar 24;16(1):200. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07520-4. PMID: 31819043 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A Nitroalkene Benzoic Acid Derivative Targets Reactive Microglia and Prolongs Survival in an Inherited Model of ALS via NF-κB Inhibition.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jan;18(1):309-325. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00953-z. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33118131 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Extraction by Response Surface Methodology Used for the Characterization and Quantification of Phenolic Compounds in Whole Red Grapes (Vitis vinifera).Nutrients. 2018 Dec 5;10(12):1931. doi: 10.3390/nu10121931. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30563177 Free PMC article.
-
Potent In Vitro Activity of Citrus aurantium Essential Oil and Vitis vinifera Hydrolate Against Gut Yeast Isolates from Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients-The Right Mix for Potential Therapeutic Use.Nutrients. 2020 May 7;12(5):1329. doi: 10.3390/nu12051329. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32392768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson NB, Hayes LD, Brown K, Hoo EC, Ethier KA. CDC National Health Report: leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors--United States, 2005–2013. MMWR Suppl. 2014;63:3–27. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Schauss AG. Mitigation of inflammation with foods. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:6703–17. - PubMed
-
- Kung H, Hoyert D, Xu J, Murphy S. Deaths: final data for 2005. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2008:56. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
