TIPE‑2 suppresses growth and aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 29568863
- PMCID: PMC5928656
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8789
TIPE‑2 suppresses growth and aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
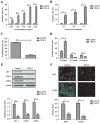
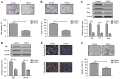
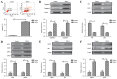
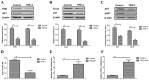
Rapid proliferation and migration are the main features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, which serve an essential role in carcinogenesis and are a hallmark of cancer therapy resistance. Previous studies have reported that tumor necrosis factor‑α‑induced protein‑8 like‑2 (TIPE‑2) is involved in cancer initiation and the progression of HCC. The present study aimed to clarify the role of TIPE‑2 in HCC carcinogenesis, growth and aggressiveness. The effects of TIPE‑2 on HCC were determined using colony forming and cell cycle analyses. Cell apoptosis, and growth and aggressiveness of HCC cells, were investigated following TIPE‑2 treatment. Treatment with TIPE‑2 markedly suppressed HCC cell proliferation and increased the number of cells in S phase of the cell cycle. The results demonstrated that TIPE‑2 significantly inhibited growth, migration and invasion of HCC cells via the downregulation of tumor metastasis-associated genes. Flow cytometric analysis indicated that TIPE‑2 promoted apoptosis of HCC cells via regulation of apoptosis‑associated gene transcription. In addition, TIPE‑2 administration downregulated the expression of phosphoinositide 3‑kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (AKT) in HCC cells. In addition, TIPE‑2 selectively decreased neuroblastoma Ras viral oncogene and p27 expression in HCC cells. In vivo assays revealed that TIPE‑2 significantly inhibited tumor growth and prolonged animal survival by promoting apoptosis of tumor cells. The results of the present study indicated that TIPE‑2 acts as an inhibitor of HCC cell growth and aggressiveness, and promotes apoptosis, thus suggesting that TIPE‑2 may inhibit the metastasis‑associated PI3K/AKT signaling cascade and may arrest the tumor cell cycle. These findings provide a potential molecular mechanism by which TIPE‑2 promotes apoptosis of HCC cells.
Keywords: tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein-8 like-2; hepatocellular carcinoma cells; apoptosis; metastasis; phospho-inositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-induced protein 8-like 2 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through inhibiting Rac1.Mol Cancer. 2013 Nov 26;12(1):149. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-149. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24274578 Free PMC article.
-
Ropivacaine suppresses tumor biological characteristics of human hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):9162-9173. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1995103. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34696683 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI3K/Akt pathway.Cancer Sci. 2017 Apr;108(4):620-631. doi: 10.1111/cas.13177. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28132399 Free PMC article.
-
Biological impact and therapeutic perspective of targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: Promises and Challenges.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Jan;187:106553. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106553. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36400343 Review.
-
Mechanism Research and Application for Ginsenosides in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 16;2023:7214037. doi: 10.1155/2023/7214037. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38027042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis reveals key genes for predicting dual-phenotype Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognosis.J Cancer. 2021 Mar 19;12(10):2993-3010. doi: 10.7150/jca.56005. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33854600 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Negative Regulator TIPE2 Inhibits Cervical Squamous Cancer Progression Through Erk1/2 Signaling.Open Life Sci. 2019 Dec 31;14:528-536. doi: 10.1515/biol-2019-0059. eCollection 2019 Jan. Open Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 33817189 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 2 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with the disease progression of chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Virol J. 2019 Oct 28;16(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1224-7. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31661000 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Roles of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Protein 8 Like-Protein 2 in Inflammation, Immunity and Cancers: A Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Dec 14;12:12735-12746. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S283877. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33364825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang YH, Wu JC, Chen SC, Chen CH, Chiang JH, Huo TI, Lee PC, Chang FY, Lee SD. Survival benefit of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 10 cm in diameter. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02704.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

