PPARα activation alleviates damage to the cytoskeleton during acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats
- PMID: 29568903
- PMCID: PMC5928683
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8771
PPARα activation alleviates damage to the cytoskeleton during acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats
Abstract
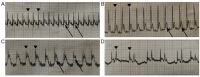
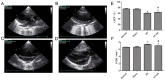
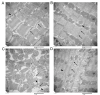
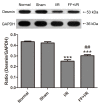
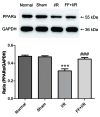
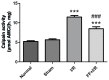
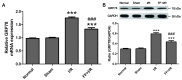
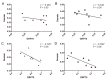
The cytoskeleton serves an important role in maintaining cellular morphology and function, and it is a substrate of calpain during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury (MIRI). Calpain may be activated by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress during MIRI. The activation of peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor α (PPARα) may inhibit ischemia/reperfusion damage by regulating stress reactions. The present study aimed to determine whether the activation of PPARα protects against MIRI‑induced cytoskeletal degradation, and investigated the underlying mechanism involved. Wistar rats were pretreated with or without fenofibrate and subjected to left anterior descending coronary artery ligation for 45 min, followed by 120 min of reperfusion. Calpain activity and the expression of PPARα, desmin and ER stress parameters were evaluated. Electrocardiography was performed and cardiac function was evaluated. The ultrastructure was observed under transmission electron microscopy. I/R significantly induced damage to the cytoskeleton in cardiomyocytes and cardiac dysfunction, all of which were improved by PPARα activation. In addition, I/R increased ER stress and calpain activity, which were significantly decreased in fenofibrate‑pretreated rat heart tissue. The results suggested that PPARα activation may exert a protective effect against I/R in the myocardium, at least in part via ER stress inhibition. Suppression of ER stress may be an effective therapeutic target for protecting the I/R myocardium.
Keywords: PPARα; cytoskeleton; desmin; acute MIRI; endoplasmic reticulum stress; calpain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of Hrd1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating PPARα to prevent oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cellular apoptosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 5;954:175864. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175864. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37392829
-
Fenofibrate protects against acute myocardial I/R injury in rat by suppressing mitochondrial apoptosis as decreasing cleaved caspase-9 activation.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Jul 4;19(4):455-463. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170572. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28582851
-
Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 5;908:174353. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174353. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34274339
-
Apelin/APJ System: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.DNA Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;35(12):766-775. doi: 10.1089/dna.2016.3391. Epub 2016 Nov 17. DNA Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27854125 Review.
-
Targeting ER stress and calpain activation to reverse age-dependent mitochondrial damage in the heart.Mech Ageing Dev. 2020 Dec;192:111380. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111380. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020. PMID: 33045249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The critical role of PPARα in the binary switch between life and death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 11;11(8):691. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02811-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32826849 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology Prediction and Pharmacological Verification Mechanism of Yeju Jiangya Decoction on Hypertension.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 May 10;2021:5579129. doi: 10.1155/2021/5579129. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34055010 Free PMC article.
-
An insight to treat cardiovascular diseases through phytochemicals targeting PPAR-α.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Mar;479(3):707-732. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04755-7. Epub 2023 May 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37171724 Review.
-
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Activation Protects Retinal Ganglion Cells in Ischemia-Reperfusion Retinas.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 23;8:788663. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.788663. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 35004756 Free PMC article.
-
4-phenylbutyric acid improves sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by modulating amino acid metabolism and lipid metabolism via Comt/Ptgs2/Ppara.Metabolomics. 2024 Apr 19;20(3):46. doi: 10.1007/s11306-024-02112-3. Metabolomics. 2024. PMID: 38641695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J, Ren F, Cheng Q, Bai L, Shen X, Gao F, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Zhai Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates liver inflammatory immune response in the pathogenesis of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplantation. 2012;94:211–217. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318259d38e. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

