Phylogeny and polymorphism in the long control regions E6, E7, and L1 of HPV Type 56 in women from southwest China
- PMID: 29568922
- PMCID: PMC5928666
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8743
Phylogeny and polymorphism in the long control regions E6, E7, and L1 of HPV Type 56 in women from southwest China
Abstract
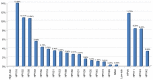
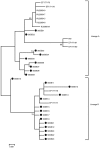
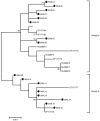
Globally, human papillomavirus (HPV)‑56 accounts for a small proportion of all high‑risk HPV types; however, HPV‑56 is detected at a higher rate in Asia, particularly in southwest China. The present study analyzed polymorphisms, intratypic variants, and genetic variability in the long control regions (LCR), E6, E7, and L1 of HPV‑56 (n=75). The LCRs, E6, E7 and L1 were sequenced using a polymerase chain reaction and the sequences were submitted to GenBank. Maximum‑likelihood trees were constructed using Kimura's two‑parameter model, followed by secondary structure analysis and protein damaging prediction. Additionally, in order to assess the effect of variations in the LCR on putative binding sites for cellular proteins, MATCH server was used. Finally, the selection pressures of the E6‑E7 and L1 genes were estimated. A total of 18 point substitutions, a 42‑bp deletion and a 19‑bp deletion of LCR were identified. Some of those mutations are embedded in the putative binding sites for transcription factors. 18 single nucleotide changes occurred in the E6‑E7 sequence, 11/18 were non‑synonymous substitutions and 7/18 were synonymous mutations. A total 24 single nucleotide changes were identified in the L1 sequence, 6/24 being non‑synonymous mutations and 18/24 synonymous mutations. Selective pressure analysis predicted that the majority of mutations of HPV‑56 E6, E7 and L1 were of positive selection. The phylogenetic tree demonstrated that the isolates distributed in two lineages. Data on the prevalence and genetic variation of HPV‑56 types in southwest China may aid future studies on viral molecular mechanisms and contribute to future investigations of diagnostic probes and therapeutic vaccines.
Keywords: human papillomavirus-56; gene polymorphism; phylogenetic trees; selection pressures.
Figures

References
-
- de Sanjose S, Quint WG, Alemany L, Geraets DT, Klaustermeier JE, Lloveras B, Tous S, Felix A, Bravo LE, Shin HR, et al. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: A retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:1048–1056. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70230-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J SI, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase. IARC; Lyon: 2013. [May 30;2012 ]. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0. No. 11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

