Taste impairment in chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 29569385
- PMCID: PMC6582951
- DOI: 10.1002/alr.22113
Taste impairment in chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: Though many patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) describe disturbances in smell and taste, there have been no studies specifically assessing taste impairment in CRS. This study sought to objectively assess taste dysfunction in CRS patients and determine whether taste impairment correlates with olfactory dysfunction. Additionally, this investigation sought to determine the impact of taste dysfunction on quality of life (QOL) in CRS and identify the clinical factors that influence taste.
Methods: Sixty-eight CRS patients were prospectively enrolled and completed several QOL surveys in relation to taste, smell, overall sinus-specific QOL, and depression. Validated taste strips were used to determine gustatory dysfunction pertaining to sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. Olfactory testing was assessed using the Sniffin' Sticks Test while both Lund-Kennedy and Olfactory Cleft Endoscopy Scoring (OCES) systems were used for endoscopic evaluation.
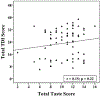
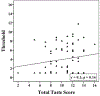
Results: The overall prevalence of dysgeusia was 28%, with scores significantly lower for sour compared to other subgroups. No correlation was observed between taste scores and objective olfactory metrics including olfaction tests and OCES. Taste scores were better in younger patients (r = 0.28, p = 0.02), female patients (p = 0.004), and never smokers compared to former smokers (p = 0.01). Taste scores did not correlate with patient-reported outcome measures or CRS disease severity metrics.
Conclusion: Taste dysfunction is a common complaint in CRS. This cohort shows prevalence of gustatory loss to be about 28% using ideal normative values. This dysfunction correlated with male gender, smoking history, and older age. Taste dysfunction did not correlate with measured olfactory outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02720653.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis; olfaction disorders; quality of life; taste; taste perception.
© 2018 ARS-AAOA, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Small DM, Green BG. A Proposed Model of a Flavor Modality. In: Murray MM, Wallace MT, eds. The Neural Bases of Multisensory Processes Boca Raton (FL), 2012. - PubMed
-
- Small DM, Prescott J. Odor/taste integration and the perception of flavor. Exp Brain Res 2005; 166:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol Jet al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 2012; 50:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

