An Autoimmune Basis for Raynaud's Phenomenon: Murine Model and Human Disease
- PMID: 29569858
- PMCID: PMC6115278
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40505
An Autoimmune Basis for Raynaud's Phenomenon: Murine Model and Human Disease
Abstract
Objective: Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) is common in anti-RNP-positive patients with rheumatic diseases but is not itself known to be caused by autoimmunity. The aim of this study was to assess autoantibodies that could mediate this process.
Methods: Antibodies derived from patient sera and from murine models of anti-RNP autoimmunity were screened for the ability to induce RP-like tissue ischemia and endothelial cell apoptosis in murine models and in vitro systems.
Results: RNP-positive sera from RP patients and murine sera from RNP-positive B cell adoptive transfer recipients induced RP-like tissue ischemia and endothelial cell apoptosis. Proteomic analysis identified cytokeratin 10 (K10) as a candidate autoantigen in RP. Monoclonal anti-K10 antibodies reproduced patterns of ischemic tissue loss and endothelial cell apoptosis; K10 knockout or depletion of anti-K10 activity in serum was protective. Cold exposure enhanced K10 expression and in vivo tissue loss.
Conclusion: Anti-K10 antibodies are sufficient to mediate RP-like ischemia in murine models and are implicated in the pathogenesis of RP in patients with anti-RNP autoimmunity.
© 2018, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any financial interests that could be perceived as being a conflict of interest. No patents pertaining to the results presented in the paper have been awarded or filed.
Figures

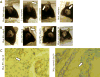
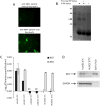


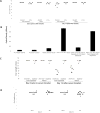
References
-
- Greidinger EL, Casciola-Rosen L, Morris SM, Hoffman RW, Rosen A. Autoantibody recognition of distinctly modified forms of the UI-70-kd antigen is associated with different clinical disease manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Amanzi L, Braschi F, Fiori G, Galluccio F, Miniati I, Guiducci S, et al. Digital ulcers in scleroderma: staging, characteristics and sub-setting through observation of 1614 digital lesions. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49:1374–82. - PubMed
-
- Chung L, Shapiro L, Fiorentino D, Baron M, Shanahan J, Sule S, et al. MQX-503, a novel formulation of nitroglycerin, improves the severity of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:870–7. - PubMed
-
- Cooke JP, Marshall JM. Mechanisms of Raynaud’s disease. Vasc Med. 2005;10:293–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

