LOX-1 deficient mice show resistance to zymosan-induced arthritis
- PMID: 29569871
- PMCID: PMC5806501
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2018.2847
LOX-1 deficient mice show resistance to zymosan-induced arthritis
Abstract
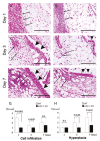
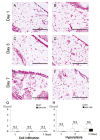
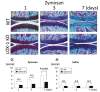
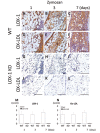
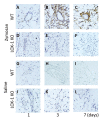
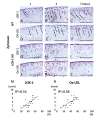
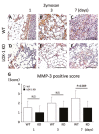
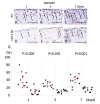
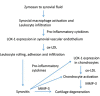
Recent data suggest that the lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) receptor-1 (LOX-1)/ox-LDL system may be involved in the pathogenesis of arthritis. We aimed to demonstrate the roles of the LOX-1/ox-LDL system in arthritis development by using LOX-1 knockout (KO) mice. Arthritis was induced in the right knees of C57Bl/6 wild-type (WT) and LOX-1 KO mice via zymosan injection. Saline was injected in the left knees. Arthritis development was evaluated using inflammatory cell infiltration, synovial hyperplasia, and cartilage degeneration scores at 1, 3, and 7 days after administration. LOX-1, ox-LDL, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) expression in the synovial cells and chondrocytes was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. The LOX-1, ox-LDL, and MMP-3 expression levels in synovial cells were scored on a grading scale. The positive cell rate of LOX-1, ox-LDL, and MMP-3 in chondrocytes was measured. The correlation between the positive cell rate of LOX-1 or ox-LDL and the cartilage degeneration score was also examined. Inflammatory cell infiltration, synovial hyperplasia, and cartilage degeneration were significantly reduced in the LOX-1 KOmice with zymosan-induced arthritis (ZIA) compared to WT mice with ZIA. In the saline-injected knees, no apparent arthritic changes were observed. LOX-1 and ox-LDL expression in synovial cells and chondrocytes were detected in the knees of WT mice with ZIA. No LOX-1 and ox-LDL expression was detected in the knees of LOX-1 KOmice with ZIA or the saline-injected knees of both mice. MMP-3 expression in the synovial cells and chondrocytes was also detected in knees of both mice with ZIA, and was significantly less in the LOX-1 KO mice than in WT mice. The positive cell rate of LOX-1 or ox-LDL and the cartilage degeneration score showed a positive correlation. Our data show the involvement of the LOX-1/ox-LDL system in murine ZIA development. LOX-1-positive synovial cells and chondrocytes are potential therapeutic targets for arthritis prevention.
Keywords: Arthritis; Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1); oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang PY, Xu X, Li XC. Cardiovascular diseases: oxidative damage and antioxidant protection. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2014;18:3091-6. - PubMed
-
- Sawamura T, Kume N, Aoyama T, Moriwaki H, Hoshikawa H, Aiba Y, et al. An endothelial receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Nature 1997;386:73-7. - PubMed
-
- Kume N, Murase T, Moriwaki H, Aoyama T, Sawamura T, Masaki T, et al. Inducible expression of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 in vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res 1998;83: 322-7. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T, Fujiwara H, Masaki T, Sawamura T. Induction of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor by oxidized LDL and lysophosphatidylcholine in cultured endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1999;31:2101-14. - PubMed
-
- Hofnagel O, Luechtenborg B, Stolle K, Lorkowski S, Eschert H, Plenz G, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines regulate LOX-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004;24:1789-95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

