The earthworm Dendrobaena veneta (Annelida): A new experimental-organism for photobiomodulation and wound healing
- PMID: 29569873
- PMCID: PMC5820523
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2018.2867
The earthworm Dendrobaena veneta (Annelida): A new experimental-organism for photobiomodulation and wound healing
Abstract
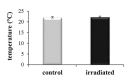
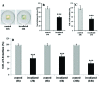
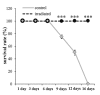
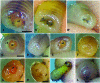
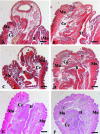
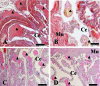
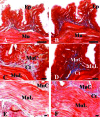
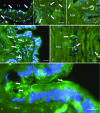
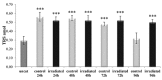
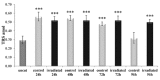
Photobiomodulation (PBM) is a manipulation of cellular behavior using non-ablative low intensity light sources. This manipulation triggers a cascade of metabolic effects and physiological changes resulting in improved tissue repair, of benefit in the treatment of tissue injury, degenerative or autoimmune diseases. PBM has witnessed an exponential increase in both clinical instrument technology and applications. It is therefore of benefit to find reliable experimental models to test the burgeoning laser technology for medical applications. In our work, we proposed the earthworm Dendrobaena veneta for the study of non-ablative laser-light effects on wound healing. In our preliminary work, D. veneta has been shown to be positively affected by PBM. New tests using D. veneta were set up to evaluate the effectiveness of a chosen 808 nm-64 J/cm2-1W-CW laser therapy using the AB2799 hand-piece with flat-top bean profile, on the wound healing process of the earthworm. Effective outcome was assimilated through examining the macroscopic, histological, and molecular changes on the irradiated posterior-segment of excised-earthworms with respect to controls. Three successive treatments, one every 24 hours, were concluded as sufficient to promote the wound healing, by effects on muscular and blood vessel contraction, decrement of bacteria load, reduction of inflammatory processes and tissue degeneration. D. veneta was demonstrated to be a reliable experimental organism that meets well the 3Rs principles and the National Science Foundation statement. Through their genetic and evolutionary peculiarity, comparable to those of scientifically accredited models, D. veneta allows the effect of laser therapies by multidisciplinary methods, at various degree of complexity and costs to be investigated.
Keywords: Heat Shock Protein; Low Level Laser Therapy; anti-inflammatory; cell proliferation.; laser irradiation; scarring; tissue repair.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest and have received no payment in preparation of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Mester E, Szende B, Tota JG. Effect of laser on hair growth of mice. Kiserl Orvostud 1967;19:628-61.
-
- Parker S. Photobiomodulation: an overview of current concepts and understanding. Benedicenti A, Benedicenti S, editors. Atlas of Laser Therapy, IV edition. Brescia, Italy; Teamwork media srl; 2016. p. 139-155.
-
- Karu T. Primary and secondary mechanisms of action of visible to near-IR radiation on cells. J Photochem Photobiol B 1999;49:1-17. - PubMed
-
- Hamblin MR, Waynant RW, Anders J, editors. Mechanisms of low level light therapy. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Proc. SPIE 6140; 2006. p 12.
-
- Karu TI, Afanas'eva NI. Cytochrome c oxidase as the primary photoacceptor upon laser exposure of cultured cells to visible and near IR-range light. Dokl Akad Nauk 1995;342:693-5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

