Hexavalents in spermatocytes of Robertsonian heterozygotes between Mus m. domesticus 2n=26 from the Vulcano and Lipari Islands (Aeolian Archipelago, Italy)
- PMID: 29569877
- PMCID: PMC5827110
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2018.2894
Hexavalents in spermatocytes of Robertsonian heterozygotes between Mus m. domesticus 2n=26 from the Vulcano and Lipari Islands (Aeolian Archipelago, Italy)
Abstract
The size and shape of the chromosomes, as well as the chromosomal domains that compose them, are determinants in the distribution and interaction between the bivalents within the nucleus of spermatocytes in prophase I of meiosis. Thus the nuclear architecture characteristic of the karyotype of a species can be modified by chromosomal changes such as Rb chromosomes. In this study we analysed the meiotic prophase nuclear organization of the heterozygous spermatocytes from Mus musculus domesticus 2n=26, and the synaptic configuration of the hexavalent formed by the dependent Rb chromosomes Rbs 6.16, 16.10, 10.15, 15.17 and the telocentric chromosomes 6 and 17. Spreads of 88 pachytene spermatocytes from two males were studied and in all of them five metacentric bivalents, four telocentric bivalents, one hexavalent and the XY bivalent were observed. About 48% of the hexavalents formed a chain or a ring of synapsed chromosomes, the latter closed by synapsis between the short arms of telocentric chromosomes 6 and 17. About 52% of hexavalents formed an open chain of 10 synapsed chromosomal arms belonging to 6 chromosomes. In about half of the unsynapsed hexavalents one of the telocentric chromosome short arms appears associated with the X chromosome single axis, which was otherwise normally paired with the Y chromosome. The cluster of pericentromeric heterochromatin mostly determines the hexavalent's nuclear configuration, dragging the centromeric regions and all the chromosomes towards the nuclear envelope similar to an association of five telocentric bivalents. These reiterated encounters between these chromosomes restrict the interactions with other chromosomal domains and might favour eventual rearrangements within the metacentric, telocentric or hexavalent chromosome subsets. The unsynapsed short arms of telocentric chromosomes frequently bound to the single axis of the X chromosome could further complicate the already complex segregation of hexavalent chromosomes.
Keywords: Hexavalents; Robertsonian chromosomes; mouse spermatocytes; nuclear architecture..
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
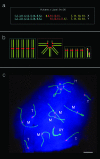
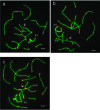
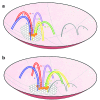
References
-
- Capanna E, Gropp A, Winking H, Noack G, Civitelli MV. Robertsonian metacentrics in the mouse. Chromosoma 1976;58:341-53. - PubMed
-
- Redi CA, Garagna S, Hilscher W, Winking H. The effects of some Robertsonian chromosome combinations on the seminiferous epithelium of the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1985;85:1-19. - PubMed
-
- Piálek J, Hauffe HC, Searle JB. Chromosomal variation in the house mouse. Biol J Linn Soc 2005;84:535-63.
-
- Capanna E, Redi CA. Whole-arm reciprocal translocation (WART) between Robertsonian chromosomes: finding of a Robertsonian heterozygous mouse with karyotype derived through WARTs. Chromosome Res 1995;3:135-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

