Prognostic significance of the dynamic changes of systemic inflammatory response in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 29570259
- PMCID: PMC6442152
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0500
Prognostic significance of the dynamic changes of systemic inflammatory response in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To elucidate the prognostic value of systemic inflammatory response in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) who are treated with sunitinib, we evaluated the prognostic role of C-reactive protein (CRP) kinetics. This study also compared prognostic models containing CRP kinetics and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) kinetics.
Materials and methods: A consecutive cohort of 94 patients with mRCC who were treated with sunitinib was retrospectively included from Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. According to dynamic changes in CRP and the NLR, patients were divided into three groups for analysis of CRP and NLR kinetics. The associations between survival and potential prognostic factors were assessed. The incremental value of prognostication was evaluated.
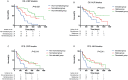
Results: A significant difference (P<0.001) in overall survival (OS) was observed among the three groups of CRP kinetics. The median OS of the non-elevated group was nearly 1.3-fold longer than that of the normalized group (33.0 vs. 26.3 months), and two times longer than that of the non-normalized group (33.0 vs. 14.0 months). Multivariate analysis showed that CRP and NLR kinetics were independent prognostic indicators. The model containing CRP kinetics had a better predictive accuracy than that with NLR kinetics, which was supported by the C-index (0.731 vs. 0.684) and the likelihood ratio χ² test (79.9% vs. 44.9%).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that dynamic changes in CRP can better predict survival in patients with mRCC who are treated with sunitinib. Routine assessment of CRP before and after targeted therapy would help identify patients at risk of a poor outcome.
Keywords: Carcinoma, Renal Cell; Molecular Targeted Therapy; Prognosis.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic impact of baseline serum C-reactive protein in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treated with sunitinib.BJU Int. 2014 Jul;114(1):81-9. doi: 10.1111/bju.12494. Epub 2014 Jan 15. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24215209
-
The effect of kinetics of C-reactive protein in the prediction of overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor.Urol Oncol. 2017 Nov;35(11):662.e1-662.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28778585
-
Prognostic Markers for Refined Stratification of IMDC Intermediate-Risk Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy.Target Oncol. 2019 Apr;14(2):179-186. doi: 10.1007/s11523-019-00634-8. Target Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30927174
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio, and C-reactive Protein as New and Simple Prognostic Factors in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018 Jun;16(3):e685-e693. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29454639
-
Epidemiology, Risk Assessment, and Biomarkers for Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Urol Clin North Am. 2020 Aug;47(3):293-303. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Urol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32600532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survival nomogram for patients with bone metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A population-based study.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Mar-Apr;47(2):333-349. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0195. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33284535 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic value of preoperative combined neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte scores in patients with renal cell carcinoma undergoing laparoscopic nephrectomy: A retrospective study.Cancer Med. 2024 May;13(9):e7214. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7214. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38686610 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 11;11:746976. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.746976. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34900692 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Systematic Review of Biomarkers in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Predictors, Prognostics, and Therapeutic Monitoring.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;15(20):4934. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204934. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLR as prognostic biomarker for metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with cytoreductive nephrectomy.Biomark Med. 2025 Mar;19(6):215-222. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2025.2471746. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Biomark Med. 2025. PMID: 40010749
References
-
- Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni JF., Jr Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA. 1999;281:1628–1631. - PubMed
-
- Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2003;30:843–852. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370:2103–2111. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–134. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2007;357:203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
