Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling in Obesity and Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 29570618
- PMCID: PMC5946184
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10040399
Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling in Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Abstract
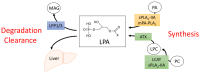
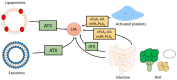
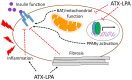
Although simple in structure, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a potent bioactive lipid that profoundly influences cellular signaling and function upon binding to G protein-coupled receptors (LPA1-6). The majority of circulating LPA is produced by the secreted enzyme autotaxin (ATX). Alterations in LPA signaling, in conjunction with changes in autotaxin (ATX) expression and activity, have been implicated in metabolic and inflammatory disorders including obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. This review summarizes our current understanding of the sources and metabolism of LPA with focus on the influence of diet on circulating LPA. Furthermore, we explore how the ATX-LPA pathway impacts obesity and obesity-associated disorders, including impaired glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: adipocytes; autotaxin; cardiovascular disease; diet; insulin resistance; lysophosphatidic acid; lysophospholipids; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

