Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Children
- PMID: 29570688
- PMCID: PMC5920390
- DOI: 10.3390/children5040044
Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Children
Abstract
Pulmonary Hypertension (PH), the syndrome of elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries, is associated with significant morbidity and mortality for affected children. PH is associated with a wide variety of potential underlying causes, including cardiac, pulmonary, hematologic and rheumatologic abnormalities. Regardless of the cause, for many patients the natural history of PH involves progressive elevation in pulmonary arterial resistance and pressure, right ventricular dysfunction, and eventually heart failure. In recent years, a number of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)-targeted therapies have become available to reduce pulmonary artery pressure and improve outcome. A growing body of evidence in both the adult and pediatric literature demonstrates enhanced quality of life, functional status, and survival among treated patients. This review provides a description of select etiologies of PH seen in pediatrics and an update on the most recent data pertaining to evaluation and management of children with PH/PAH. The available evidence for specific classes of PAH-targeted therapies in pediatrics is additionally discussed.
Keywords: pediatrics; pulmonary arterial hypertension; pulmonary hypertension; review.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Colorado contracts with Actelion, Bayer, Lilly and United Therapeutics for Ivy to be a consultant.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Pediatric Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2020 Oct;67(5):903-921. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2020.06.005. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32888689 Review.
-
Why there is a need to discuss pulmonary hypertension other than pulmonary arterial hypertension?World J Crit Care Med. 2015 Nov 4;4(4):274-7. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v4.i4.274. eCollection 2015 Nov 4. World J Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 26557477 Free PMC article.
-
Right Ventricular and Right Atrial Function Are Less Compromised in Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Comparison With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension With Similar Pressure Overload.Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Feb;15(2):e008726. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008726. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Circ Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 34937392 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric pulmonary hypertension.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Jul;21(10):1253-1268. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1757071. Epub 2020 May 13. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32401622 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for pulmonary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 31;1(1):CD012621. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012621.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30701543 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Expression and clinical significance of circular RNA hsa_circ_0003416 in pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24273. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24273. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35165927 Free PMC article.
-
Use of pulmonary vasodilators in Fontan patients: a useful strategy to improve functional status and delay transplantation?Pulm Circ. 2018 Jul-Sep;8(3):2045894018798616. doi: 10.1177/2045894018798616. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pulm Circ. 2018. PMID: 30124131 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Echocardiographic Changes and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Pediatric Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Treated With Bosentan for 72 Weeks: A Post-hoc Analysis From the FUTURE 3 Study.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jun 16;9:681538. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.681538. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34222150 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Definitions, Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment.Compr Physiol. 2021 Jun 30;11(3):2135-2190. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c200023. Compr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34190343 Free PMC article.
-
Missed or Delayed Diagnosis of Heart Disease by the General Pediatrician.Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;12(3):366. doi: 10.3390/children12030366. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
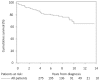
- D’Alonzo G.E., Barst R.J., Ayres S.M., Bergofsky E.H., Brundage B.H., Detre K.M., Fishman A.P., Goldring R.M., Groves B.M., Kernis J.T., et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991;115:343–349. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-5-343. - DOI - PubMed
-
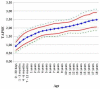
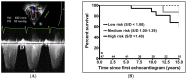
- Zijlstra W.M., Douwes J.M., Rosenzweig E.B., Schokker S., Krishnan U., Roofthooft M.T.R., Miller-Reed K., Hillege H.L., Ivy D.D., Berger R.M.F. Survival differences in pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension: Clues to a better understanding of outcome and optimal treatment strategies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;63:2159–2169. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.575. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

