Cigarette smoke enhances oncogene addiction to c-MET and desensitizes EGFR-expressing non-small cell lung cancer to EGFR TKIs
- PMID: 29570930
- PMCID: PMC5928373
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12193
Cigarette smoke enhances oncogene addiction to c-MET and desensitizes EGFR-expressing non-small cell lung cancer to EGFR TKIs
Abstract
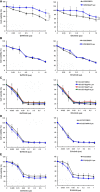
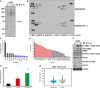
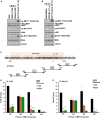
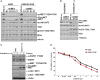
Cigarette smoking is one of the leading risks for lung cancer and is associated with the insensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, it remains undetermined whether and how cigarette smoke affects the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR TKIs. In this study, our data showed that chronic exposure to cigarette smoke extract (CSE) or tobacco smoke-derived carcinogen benzo[α]pyrene, B[α]P, but not nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone (NNK), reduced the sensitivity of wild-type EGFR-expressing NSCLC cells to EGFR TKIs. Treatment with TKIs almost abolished EGFR tyrosine kinase activity but did not show an inhibitory effect on downstream Akt and ERK pathways in B[α]P-treated NSCLC cells. CSE and B[α]P transcriptionally upregulate c-MET and activate its downstream Akt pathway, which is not inhibited by EGFR TKIs. Silencing of c-MET reduces B[α]P-induced Akt activation. The CSE-treated NSCLC cells are sensitive to the c-MET inhibitor crizotinib. These findings suggest that cigarette smoke augments oncogene addiction to c-MET in NSCLC cells and that MET inhibitors may show clinical benefits for lung cancer patients with a smoking history.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; benzo[α]pyrene; c-MET; cigarette smoke; lung cancer.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Adams JD, O'Mara‐Adams KJ and Hoffmann D (1987) Toxic and carcinogenic agents in undiluted mainstream smoke and sidestream smoke of different types of cigarettes. Carcinogenesis 8, 729–731. - PubMed
-
- Askari MD, Tsao MS and Schuller HM (2005) The tobacco‐specific carcinogen, 4‐ (methylnitrosamino)‐1‐ (3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanone stimulates proliferation of immortalized human pancreatic duct epithelia through beta‐adrenergic transactivation of EGF receptors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 639–648. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beau‐Faller M, Ruppert AM, Voegeli AC, Neuville A, Meyer N, Guerin E, Legrain M, Mennecier B, Wihlm JM, Massard G et al (2008) MET gene copy number in non‐small cell lung cancer: molecular analysis in a targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor naïve cohort. J Thorac Oncol 3, 331–339. - PubMed
-
- Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Haserlat SM, Harris PL, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Sgroi DC, Muir B, Riemenschneider MJ, Iacona RB et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non‐small‐cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. J Clin Oncol 23, 8081–8092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

