Dose-dependent reduction in cocaine-induced locomotion by Clozapine-N-Oxide in rats with a history of cocaine self-administration
- PMID: 29571824
- PMCID: PMC5899660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.03.045
Dose-dependent reduction in cocaine-induced locomotion by Clozapine-N-Oxide in rats with a history of cocaine self-administration
Abstract
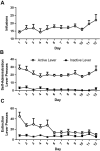
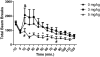
Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADDs) are novel tools for the dissection of circuitry mediating behavior and neural function. Designer receptors based on the muscarinic M3 and M4 subtypes were designed to be activated by clozapine-N-oxide (CNO), a ligand previously shown to be an inert metabolite of clozapine. However, recent work in rats has shown that CNO is reverse metabolized to its parent compound. Furthermore, CNO administration (5 mg/kg IP) attenuates amphetamine-induced locomotion and the evoked dopamine response that accompanies it. As these systems are routinely used to probe the neurocircuitry underlying cocaine-seeking behavior, here we sought to determine whether CNO would have similar effects on cocaine-induced locomotion in rats with a history of cocaine self-administration. In order for muscarinic-based DREADDs to be utilized for the dissection of circuitry underlying behavioral responses to cocaine, the doses of CNO administered to induce DREADD signaling must themselves have no effect on cocaine-induced behavior. Male Sprague-Dawley rats self-administered cocaine (0.35 mg/infusion) for 12 days, followed by 14-21 days of instrumental extinction training. Rats then underwent locomotor testing. CNO (0, 3, or 5 mg/kg) was injected (utilizing a within-subjects design), followed 20 min later by cocaine (10 mg/kg IP). Locomotion was monitored for the following 120 min. We found that the 5, but not the 3 mg/kg, dose of CNO reduced cocaine-induced locomotion. Thus, studies utilizing DREAADs to probe cocaine-induced behavior should consider these findings when choosing a dose of CNO and include non-DREADD CNO controls.
Keywords: Addiction; CNO; Circuitry; DREADDs; Reinstatement; Relapse.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clozapine N-Oxide Administration Produces Behavioral Effects in Long-Evans Rats: Implications for Designing DREADD Experiments.eNeuro. 2016 Nov 1;3(5):ENEURO.0219-16.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0219-16.2016. eCollection 2016 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2016. PMID: 27822508 Free PMC article.
-
Gq-DREADD Selectively Initiates Glial Glutamate Release and Inhibits Cue-induced Cocaine Seeking.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 1;78(7):441-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.016. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25861696 Free PMC article.
-
Does chronic systemic injection of the DREADD agonists clozapine-N-oxide or Compound 21 change behavior relevant to locomotion, exploration, anxiety, and depression in male non-DREADD-expressing mice?Neurosci Lett. 2020 Nov 20;739:135432. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135432. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 33080350
-
Modulating Dopamine Signaling and Behavior with Chemogenetics: Concepts, Progress, and Challenges.Pharmacol Rev. 2019 Apr;71(2):123-156. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.013995. Pharmacol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30814274 Review.
-
Novel designer receptors to probe GPCR signaling and physiology.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jul;34(7):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.04.006. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23769625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amygdalo-nigral circuit mediates stress-induced vulnerability to the parkinsonian toxin MPTP.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jul;29(7):1940-1952. doi: 10.1111/cns.14151. Epub 2023 Mar 13. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 36914579 Free PMC article.
-
Off-Target Effects of Clozapine-N-Oxide on the Chemosensory Reflex Are Masked by High Stress Levels.Front Physiol. 2019 May 22;10:521. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00521. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31178741 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function differences in the prelimbic cortex to basolateral amygdala circuit mediate trait vulnerability in a novel model of acute social defeat stress in male mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Feb;47(3):788-799. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01229-6. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 34799681 Free PMC article.
-
Deschloroclozapine exhibits an exquisite agonistic effect at lower concentration compared to clozapine-N-oxide in hM3Dq expressing chemogenetically modified rats.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 30;17:1301515. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1301515. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38099201 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Methamphetamine Self-Administration and Extinction on Astrocyte Structure and Function in the Nucleus Accumbens Core.Neuroscience. 2019 May 15;406:528-541. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.03.040. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30926546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves-Rodrigues A, Leurs R, Willems E, Timmerman H. Binding of clozapine metabolites and analogues to the histamine H3 receptor in rat brain cortex. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 1996;329:413–416. - PubMed
-
- Lin G, McKay G, Midha KK. Characterization of metabolites of clozapine N-oxide in the rat by micro-column high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with electrospray interface. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1996;14:1561–1577. - PubMed
-
- Jann MW, Lam YW, Chang WH. Rapid formation of clozapine in guinea-pigs and man following clozapine-N-oxide administration. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1994;328:243–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

