The use of tDCS as a therapeutic option for tinnitus: a systematic review
- PMID: 29573997
- PMCID: PMC9452266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2018.02.003
The use of tDCS as a therapeutic option for tinnitus: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Due to the subjectivity of the tinnitus diagnosis and its diverse etiologies, establishing an effective treatment is complex. In this context, transcranial direct current stimulation, a noninvasive option, is available for most patients and has shown good results in the treatment of other symptoms such as chronic pain.
Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic response of tinnitus to transcranial direct current stimulation.
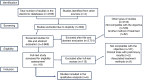
Methods: A systematic review of the literature was performed using the following descriptors: tinnitus, transcranial direct current stimulation and randomized clinical trial. The research was carried out in the MEDLINE/PUBMED, Lilacs, and Scielo databases. The inclusion criteria were: patients over 18 years of age with no associated comorbidities, who had a diagnosis established by a specialist or through the application of previously validated scales and criteria applied by a non-specialist physician.
Results: A total of 4165 studies were found, and a total of six were selected after the inclusion criteria were applied, obtaining a sample of 602 patients. Based on the defined criteria, there was a positive response to transcranial direct current stimulation in 14.86% of the participants.
Conclusion: Based on literature studied, there is no therapeutic response of tinnitus to transcranial direct current stimulation.
Introdução: Devido à subjetividade do diagnóstico do zumbido e a suas diversas etiologias, o estabelecimento de um tratamento eficaz é complexo. Neste contexto surge a transcranial direct current stimulation, uma opção não invasiva, acessível para grande parte dos pacientes, e que tem apresentado bons resultados no tratamento de outros sintomas como dor crônica.
Objetivo: Avaliar a resposta terapêutica do zumbido ao transcranial direct current stimulation.
Método: Foi realizada uma revisão sistemática da literatura, por meio dos seguintes descritores: zumbido, transcranial direct current stimulation e ensaio clínico randomizado. A pesquisa foi realizada nas bases de dados MEDLINE/PubMed, Lilacs, Scielo. Os critérios de inclusão foram: pacientes maiores de 18 anos sem outras comorbidades associadas, que tiveram diagnóstico estabelecido por um especialista ou por meio da aplicação de escalas e critérios previamente validados aplicados por médico não especialista.
Resultados: Foram encontrados 4.165 estudos, sendo selecionado após a aplicação dos critérios de inclusão um total de seis, obtendo-se uma amostra de 602 pacientes. A partir dos critérios definidos, houve uma resposta positiva ao transcranial direct current stimulation em 14.86% dos participantes.
Conclusão: Baseada na presente revisão, não há ainda uma resposta terapêutica do zumbido ao transcranial direct current stimulation.
Keywords: Estimulação transcraniana direta; Tinnitus; Transcranial direct current stimulation; Zumbido; tDCS.
Copyright © 2018 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
References
-
- Rider D., Vanneste S., Weisz N., Londero A., Schlee W., Elgoyhen A., et al. An integrative model of auditory phantom perception: tinnitus as a unified percept of interacting separable sub networks. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;44:16–32. - PubMed
-
- Lissi P., Amaral N., Oliveira P. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul; Porto Alegre: 2006. Estudo da prevalência e das características em trabalhadores expostos a ruído ocupacional. [dissertação]
-
- Kalu U.G., Sexton C.E., Loo C.K., Ebmeier K.P. Transcranial direct current stimulation in the treatment of major depression: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2012;42:1791–1800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical